Online Quiz
The Origin and Early Evolution of the earth
Distribution of the elements
Only ¼ of 100 known elements are common
> 95% of the universe being composed of only the 2 lightest elements (H & He)
15-20 elements can be called constituents of the earth, & some aren’t very conspicuous
major elements in solid earth & meteorites: H, C, N, neon Ne, & argon Ar
Helium (He) is almost totally missing from the earth because it has been lost to space
why is there any H (lighter than He!)? Because much of the earth‘s original H combining with O to make relatively heavy water molecules
The abundance of water is the most unique chemical characteristic of the earth
Probable Origin of the Earth
1. Buffon hypothesis gravitational pull of passing comets had torn away hot masses from sun, then cooled to form planets
– rejected because:
So many near collisions are improbable
Comets have very week gravity fields
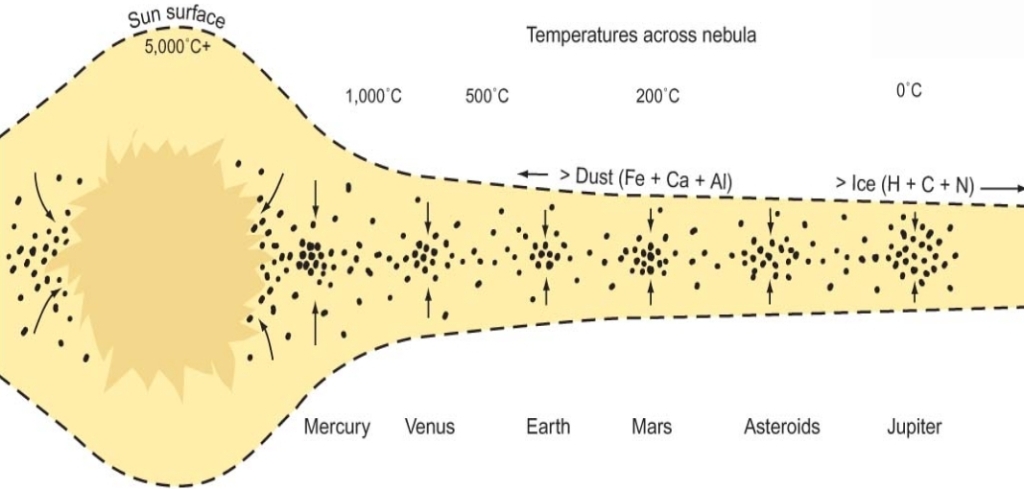
2. Solar nebula condensation of the planets from a hot, gaseous cloud (surrounding the sun) rather than their being derived from the sun itself
3. aggregation of cold clouds of dust & gases after 1900, the internal heating of the earth occurred after its aggregation, The energy produced by such heating continues to disturb the earth, as evidenced by earthquakes, volcanoes, & mountains
4. Planetesimal hypothesis: first important suggestion of a cold origin of the planets, close passage of another star past our sun, The pull of intruder‘s gravity field extracted solar gaseous material, which first condensed in space to form small, & solid bodies (planetesimals) & Then number of these cold asteroid-like aggregated to form planets
In the mid-20th century, von Weizacker & Kuiper modified the planetesimal concept they tried to explain the simultaneous origin of the entire solar system in a unified nebular hypothesis
nebular hypothesis

1. Planetesimal: small bodies from dust &gas
2.Protoplanets 9-10 formed by planetesimals
3. Planet formed by combining protoplanets swept up by gravitational attraction
Heat & Composition distribution
– estimated from physical chemical theory applied to the mineral phases
– observed in meteorites

The density & T increases with depth
Crust → solid & Cold,7-70Km
Mantle → lower 2900-660Km,upper 660-410
outer core → liquid, 5150-2900Km
Innre core → solid & very hot, 6270-5150Km
Note. discontinuity at core-mantle boundary

relation of the upper mantle to subduction zone, midocean ridge, & the region where basaltic magma forms
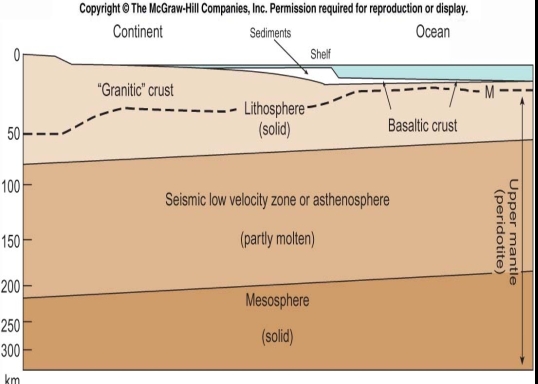
The moho (M) was previously taken to be the boundary between the crust & upper mantle, It is basically a seismic anomaly
The zones shown here are based on analysis of seismic velocities from earthquakes
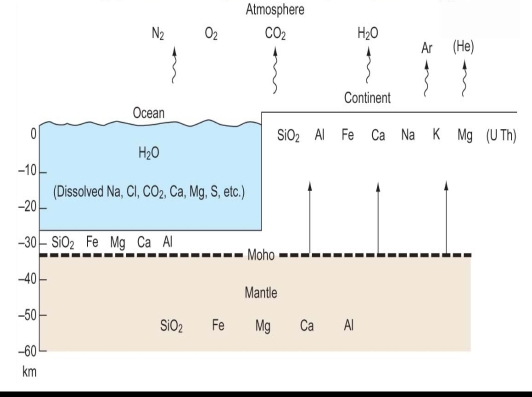
Present distribution of major elements & U, Th, He, Ar in atm, crust, & seawater
(abundanece are decreasing from left to right)
Atmosphere
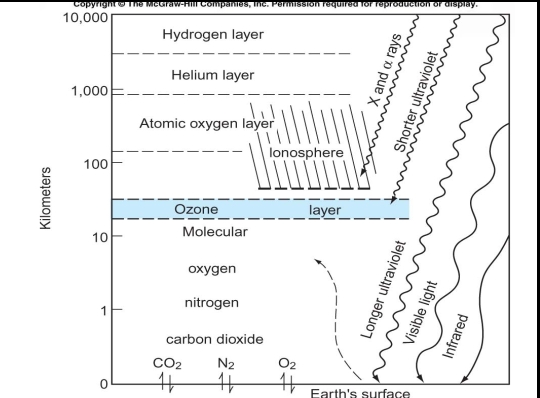
of Radiation & Radiation Shields
density stratification with regard to the gases (lightest farthest & heaviest closer to surface)
vertical scale is logarithmic

1. changes from Stage I to II, the evolution of (N), & virtual disappearance of H & CH₄, 4.5Ga
2. The change from II to III was rise in O (due to evolution of photosynthetic algae), 4.5-3Ga
presence of the noble gases (Ar, Ne, He, Kr) Most likely from the degassing upper mantle which continues to today
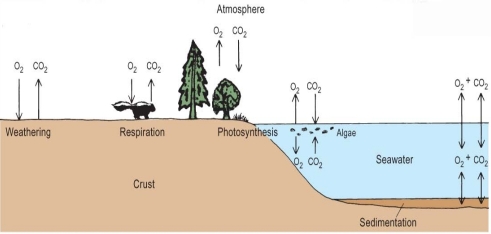
This diagram shows the important flows for O, & C though not reduced C, & Other elements (N, P, S, Na, Ca, K) follow similar cycles
Chemostat: hold chemistry constant or change slowly)
Start analyzing cycle with the algae (as prime movers)
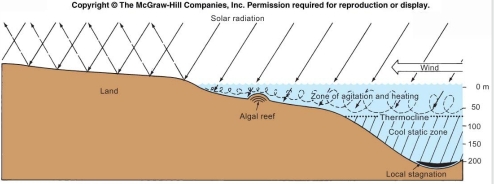
Shallow water is heated by the sun to form the Earth’s most important heat reservoir
The photic zone above the thermocline is the habitat of algae & phytoplankton
Below thermocline water cooler, less agitated so less oxygenated, & These waters may even become stagnant & reducing
When they do they constitute the first step in the preservation of organic matter, which eventually leads to gas & oil deposits
