The Later Ordovician
The Ordovician Life
cover the time from 490-442MY ago (460-442)
In this period an explosive radiation of the Paleozoic had been take place, so Ordovician marine life was dramatically different from that of the Cambrian
the difference between Ordovician & Cambrian:
1. diversity: Only 150 families of animals are known from Cambrian, but by the Late Ordovician there were > 400 families
2. diversity is consequence of much greater ecological complexity: The simple Cambrian food chain of deposit-feeding trilobites & a few suspension feeders was replaced by a complex food chain
3. Ecological tiering increased: In Cambrian only few sponges & archaeocyathids protruded more than a few centimeters above the bottom, & in Ordovician several types of organisms reached half a meter or more above the sea floor

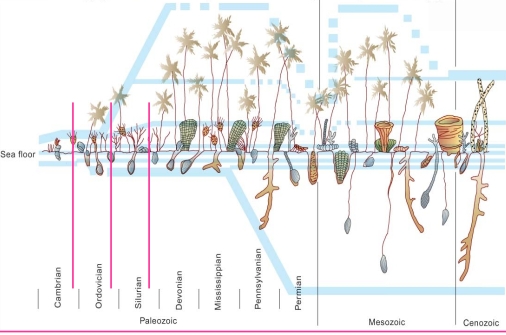
Cambrian: most invertebrates few cm above sea floor or were very shallow burrowers
Ordovician: crinoids & branching bryozoan began to take advantage of food-bearing currents up to 3m above sea floor
Ordovician life showed a much higher level of ecological complexity than any previous time in geologic history
Examples:
Primary producers (algae) grazed by snails
Microscopic plankton fed upon by a wide array of filter feeders
Trilobites scavenged detritus on bottom
The top predators were the giant straight- shelled nautiloids, when they died, nutrients were recycled back into the food chain by bacterial decay
The most common fossils In Ordovician
1. Articulate brachiopods
2. Bryozoans
3. Crinoids
4. Coral reefs
5. Nautiloides
6. Snails or gastropods
7. Graptolites
Articulate brachiopods
it differ from the inarticulate brachiopods which dominate the Cambrian by:
1. Articulate brachiopods had teeth & sockets in their hinge area to keep the shells better connected, in inarticulate the shells held together by muscles only
2. Articulate shells formed from CaCO₃, while phospate used by inarticulate.
2 groups of Articulate are characterized the Ordovician:
1. Orthids
2. Strophomenids


Bryozoans
colonial animals that form coral-like skeleton with thousands of tiny holes.
Each of these pinhole-sized chambers houses a tiny filter-feeding animal
Crinoids
are echinoderms related to sea stars.
Cambrian stalked echinoderms were primitive animals known as eocrinoids, in Ordovician, they were replaced by the major groups of crinoids typical of rest Paleozoic



Coral reefs
in the Cambrian, archaeocythids & sponges formed reef like mounds, but these mounds were never as large or diverse as coral reef
In the Late Ordovician, 2 groups of corals became the dominant reef builder:
1. The rugosids or ‘horn corals’
2. The tabulates or ‘honeycomb corals’


Nautiloides
the large Ordovician predator
about 10m in length, while the largest predator in the Cambrian was 45cm long
By the Early Ordovician nautiolides were abundant worldwide, so the Cambrian Trilobite must have Been a favorite prey item, Therefore the trilobite are much less common in the Ordovician than Cambrian
Snails or gastropods
evolved from the Cambrian Molluscus
Coiled in 2 ways:
1. Plane coiling
2. spiral coiling along axis

Graptolites
their name means ‘written on stone’
in recent years, these animals have been found preserved in 3D in limestone
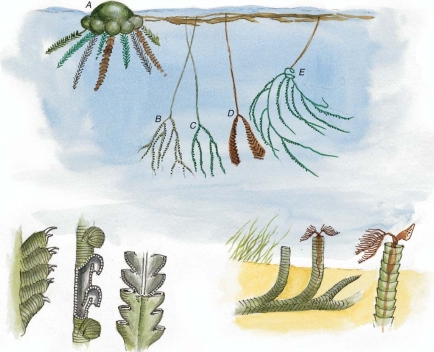
Graptolites was worldwide distributed & evolved rapidly, that why they are the best index fossils in the Ordovician time
Great Radiation
the Ordovician marked a great radiation of many groups of animals
radiation increased the diversity & the ecological complexity of shallow-marine communities
What is causes of great Ordovician radiation which established the Paleozoic fauna?
The late Cambrian & Ordovician marked the highest sea levels up to that point (the Ordovician time), This mean, continents was almost completely flooded, forming a large area of shallow seas in which marine life could diversify
O₂ levels increased in the Vendian, Cambrian, & several evidences, & finally reached modern levels (20%) in Ordovician
Ordovician Extinctions
The end of the Ordovician marked one of the most great mass extinction episodes in the history of life
> 100 families of marine animals did not make it into the Silurian
> half the species of brachiopods & bryozoans died out
The Crinoid, stromatoporoid, tabulate, rugosid, receptaculitid reef community was decimated & did not recover until late in the Silurian Period
Nautiloids were also decimated, & trilobites declined even further
Most striking fact about these extinctions:
1. The extinctions were concentrated in tropical groups
2. The survivors & replacements were adapted either to deep waters or to cold waters from high latitudes
Based on the last striking facts, the Ordovician extinctions May resulted from a severe cooling event in the world ocean in the Ordovician, this cause was deduced from the major glaciation of the southern Gondwana super continent, centered in N-Africa
Cooled climate enable only cold-adapted
invertebrates could survive to repopulate sea floor in the Silurian
Stratigraphy of the Pre Cambrian & Paleozoic in Jordan
The Pre Cambrian Rocks:
Exposed in small area from Jordan, in:
1. Aqaba
2. the eastern rim of Wadi Araba
3. Wadi Rum
4. al Queira area
These rocks are represented by:
1. Igneous rocks: granite, granodiorite, quartz diorite, hornblendite, basic dykes, & acidic dykes
2. Metamorphic rocks: gneiss, schist, & Sarmuj conglomerates
The most northern exposure of these rocks near the southern end of the dead Sea, (wadi Abu Burqa)
The Paleozoic rock exposures in Jordan
The Paleozoic rocks are failed in 2 Groups:
1. Ram Group: subdivided into 6 Formations
2. Khreim Group: subdivided into 4
Ram Group
1. Salib Akosic Sandstone formation
2. Burj Dolomite-Shale formation
3. Abu Khusheiba Sandstone formation
4. Umm Ishrin Sandstone formation
5. Disi Sandstone formation
6. Umm Sahm Sandstone formation
Khreim Group
1. Hiswah Sandstone formation
2. Dubaydib Sandstone formation
3. Mudawara Sandstone formation
4. Khushsha Sandstone formation

