Chapter 7 : Geology 101
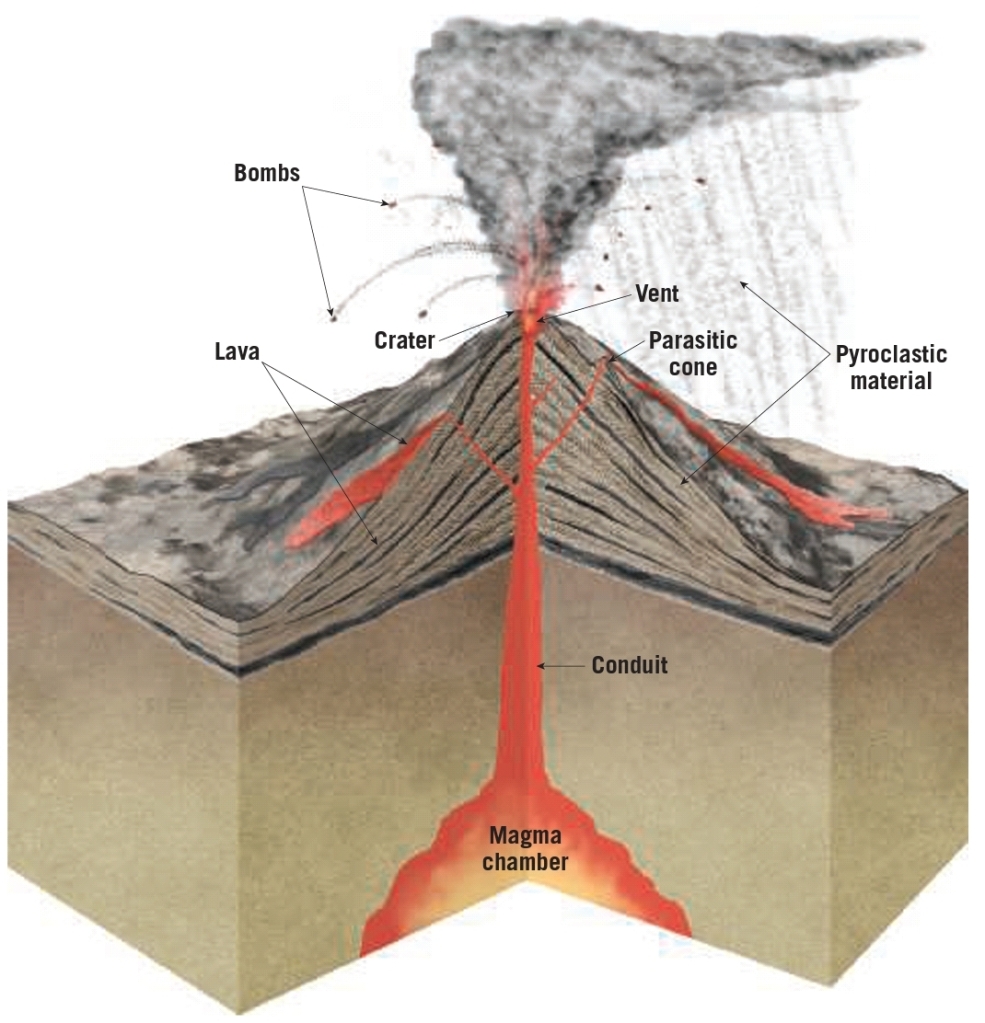
Volcano
Volcano is a mountain formed of lava & pyroclastic materials
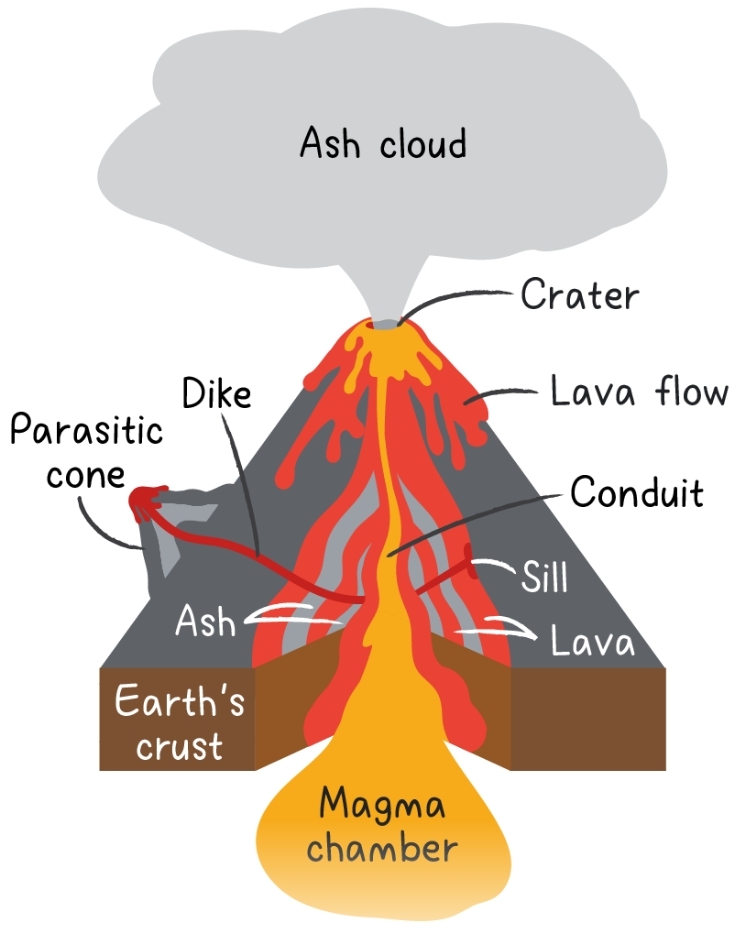
Crater depression at a summit of a volcano
Caldera is a Crater with depression> 1 km
– Nearly circular
– formed by collapse
Conduct (pipe) carries magma to the surface where it’s extruded from a surface opening called a vent
– connects magma chamber to the surface
– rare type to depth 200km in S Africa
– necks Volcanoes on land weathered, eroded, but in pipe is more resistant & remain standing for a long while & is named neck
Vent opening in the surface via which molten rocks & gases are released
Fumaroles Vents that emit only gases
Parasitic Cones produced by volcanic activity from fissures along the flanks
Volcanoes
Violent Volcanoes: ring of fire, produce Pyroclectic materials
Quite Volcanoes: produce lava, like Hawaii
Lava flow
– It comes out from the quiet volcanoes
– 90% by volume are basaltie in composition
Pahaoehoe (ropy) Lava
– It’s name comes from Hawaii
– 10 to 300 m/hr
– Resembles braids in ropes
– control: fire boats
Aa lava
– It’s name comes from Hawaii
– 5m/hr
– Rough , jagged blocks
Viscosity
Is The measure of a material’s resistance to flow
Eruptions & Viscosity determine by
1. Composition of the magma
Granitic, Andisitic, or Basaltic
2. Temperature of the magma
3. Dissolved gasses in the magma
– gas 1 – 5 % by weight
– H₂O 70%, CO₂ 15%, N₂ & SO₂ 10%, Cl₂,H₂, Ar
– provide the force to extrude lava
– gas are expand near the surface


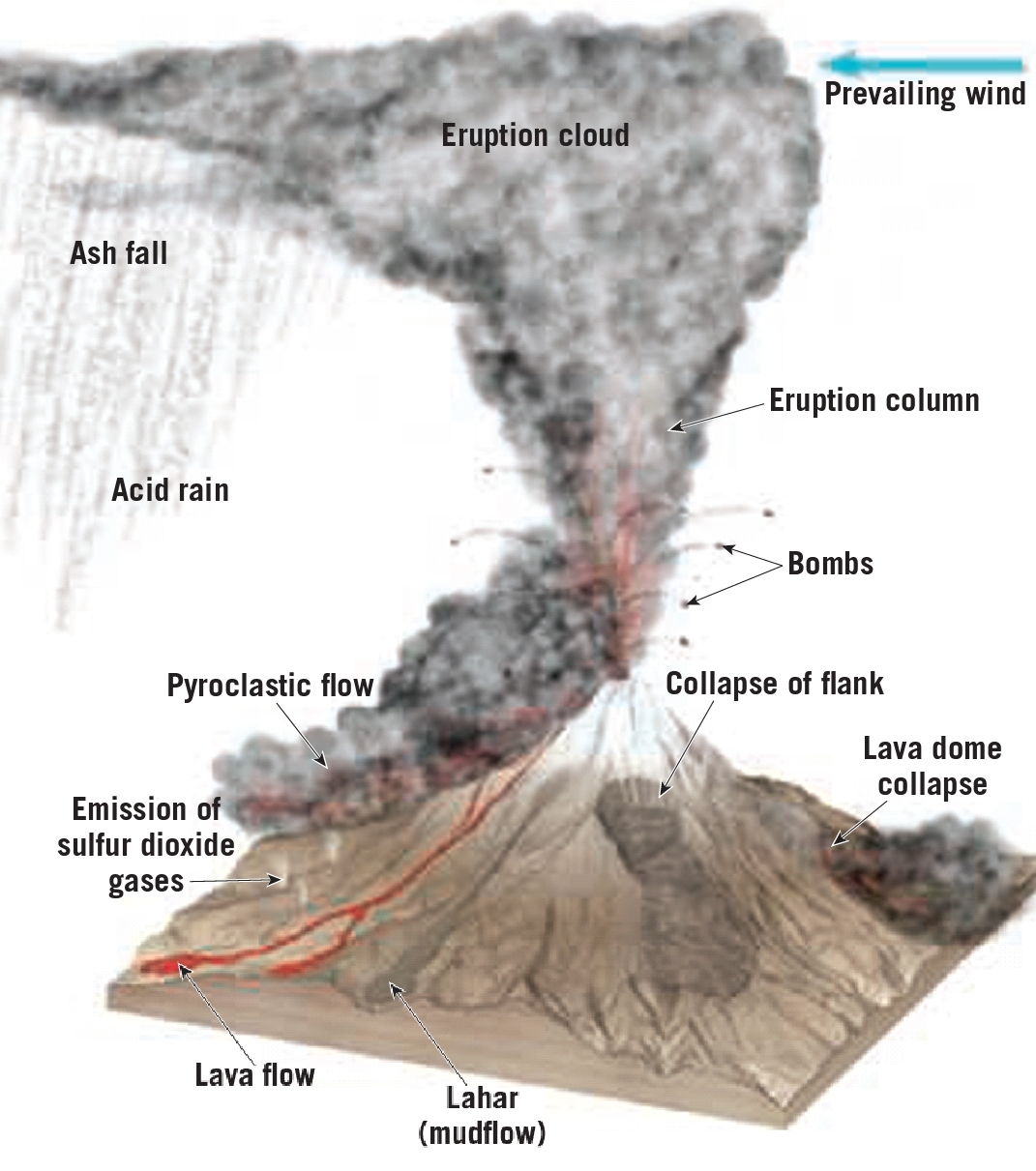
comes out from the violent volcanoes.
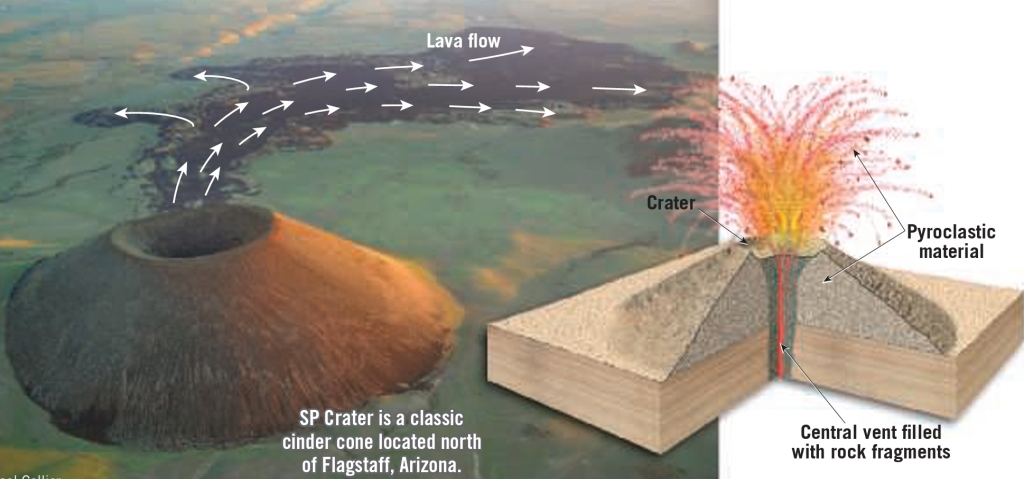
Those are ejected pulverized rocks , lava & glass fragments
Blocks if made of hardened lava
Bombs if lava twisted after ejected in the air
Volcanic structures & eruptive styles
Shield volcanoes broad, gently sloping, built from fluid basaltic lava
– Hawaiian islands (MaunaLoa) > 9km high
– Flanks have gentle slopes of a few degrees
Cinder cones small, built of pyroclastic materials ejected from a single vent
– They have a steep slope angle
– Frequently occur in groups
Composite cones (strato voleanoes) composed of inter bedded lava flows & pyroclastic materials
– located around pacific ocean (ring of fire)
– Large conical shape with steep summit
– more gradually sloping flanks
– Magna gas-rich with andesitic composition
– Most violent type of activity (explosive)
– Ex: Saint Helens, Andes mountains
– most destructive because of:
1. Pyroclastic flow (hot gas + Ash) which move down slope with speed 200Km/hr
2. Lahars (mud flow)
Fissures eruptions Volcanic materials are extruded from fractures in the crust
– Long narrow cracks emit low-viscosity fluid of basaltic lava termed fluid basalts
– Landscape buried by these lava produce basalt plateaus
Intrusive igneous activity
Plutons (Intrusions) are structures that result from the emplacement of magma into preexisting rocks beneath the earth surface
Intrusive igneous bodies (Plutons) are classified according to shape & orientation with respect to the host rock
Tabular intrusive bodies
Sills are horizontal concordant bodies where magma is insetal between sedimentary beds
– can change into discordant (Dike) by change there orientation
Dikes are discordant bodies that cut acoss bedding surfaces in the host rock
– can change into concordant (Sill) by change there orientation
Massive intrusive bodies
Batholiths largest intrusive bodies, usually felsic or intermediate rock, discordant
– can change into concordant (laccolith) by change there orientation
Laccolith igneous body, injected betweem sedimeniary strata & arcs the beds above
– can change into discordant (Batholiths) by change there orientation
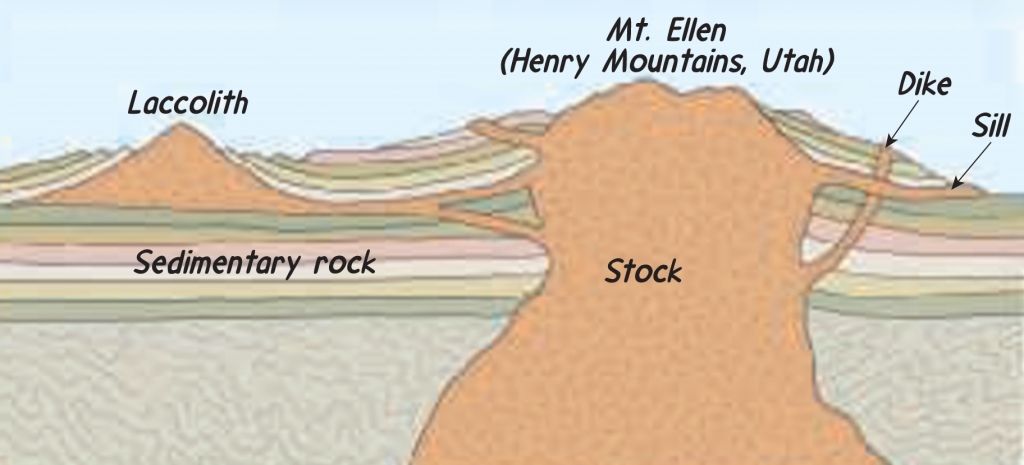
Dike tabular, discordant , low Viscosity, Basaltic
Laccolith massive, concordant, high Viscosity, Granitic
Batholith massive, discordant, high Viscosity, Granitic
Plate tectonics & igneous activity
Most active volcanoes are
– composite cones, emit volatile-rich magma
– having intermediate composition
– located along the margins of ocean, within circum, pacific belt
Deep ocean basins, include oceanic ridges & basaltic shield volcanoes (Hawaii)
we can find all volcanoes types in Interior of the continents
Zones of igueous activity
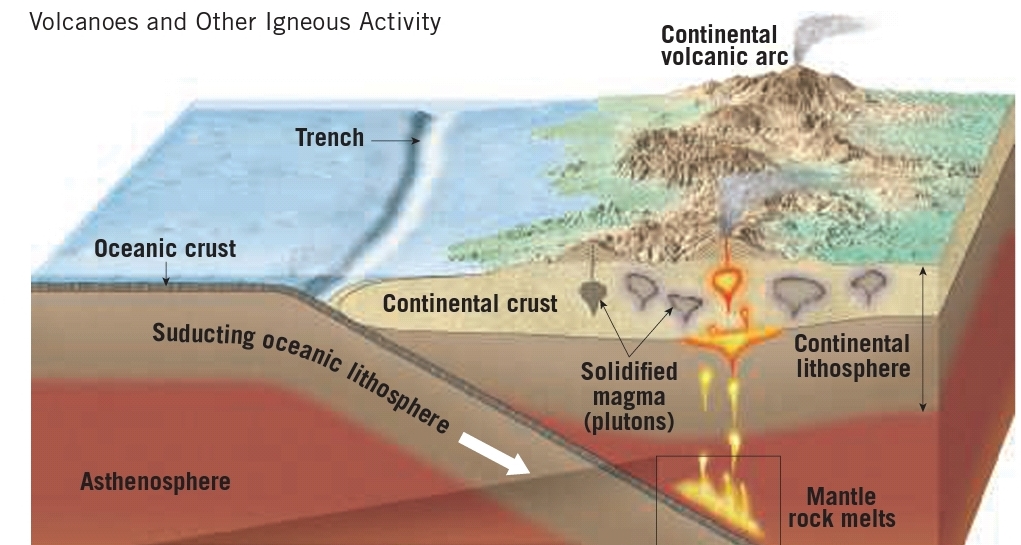
Voleanism at convergent boundaries
– Subduction of oceanic slab triggers partial melting in upper mantle at depth of 100 km
– Partial melting caused by addition of volatiles (water) derived from the sunducting plate
– Volcanie island ares such as Marianns & coutinental volcanic ares are formed (Andes)
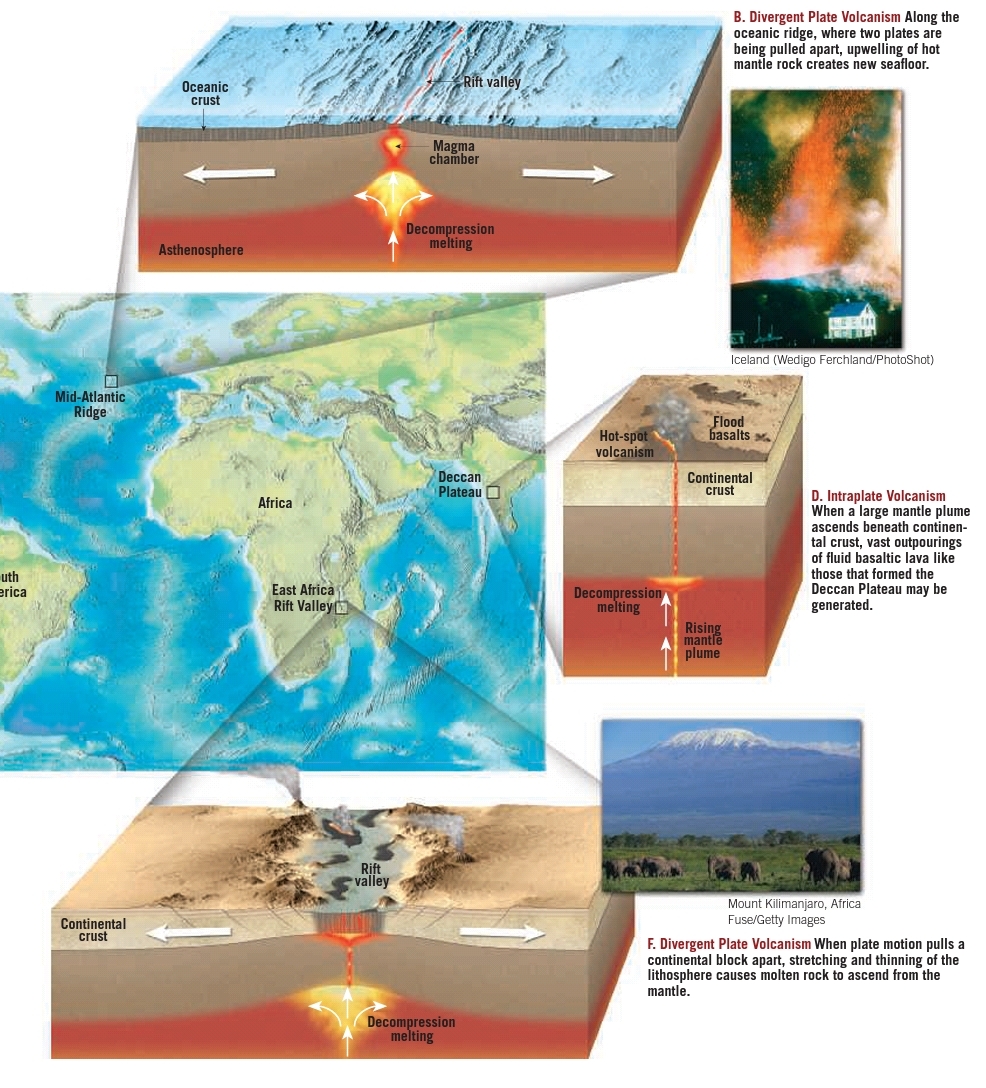
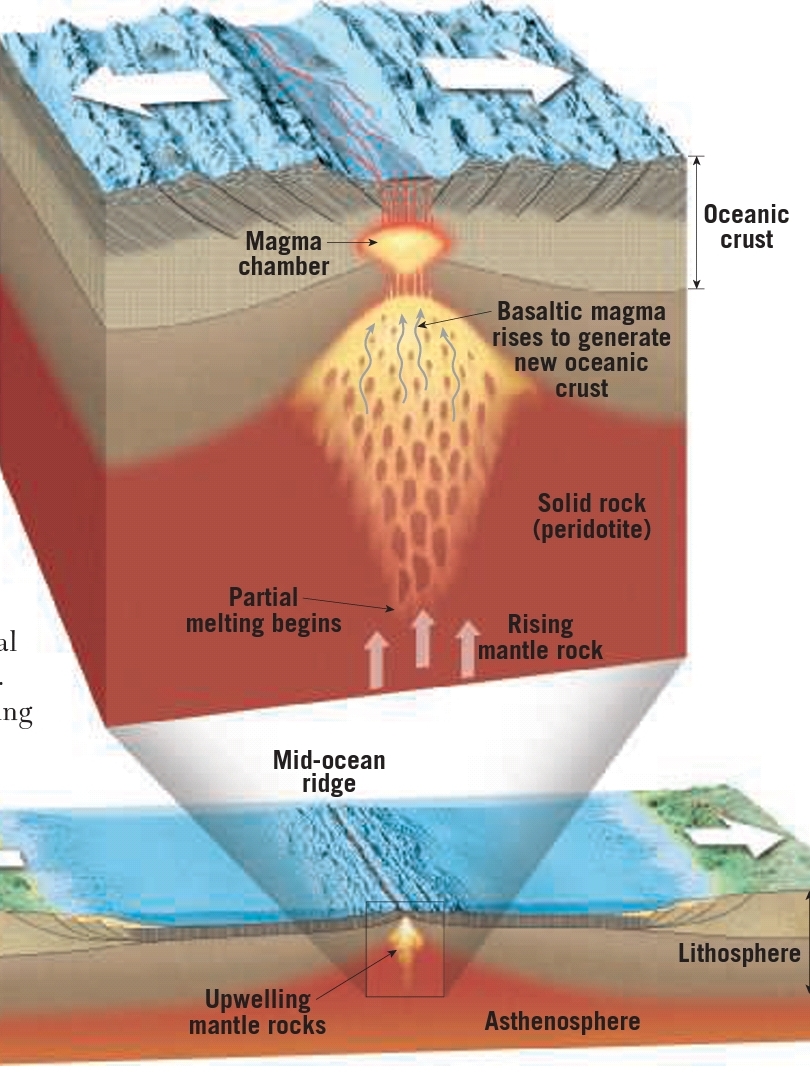
Volcanism at divergent boundaries
– Greatest volume of magma (60%) is produced along oceanic ridge system
– Tensional forces in the lithosphere causes reduction of confining pressure in the mobile mantle triggering decompression melting
– Partial melting produces basaltic magma
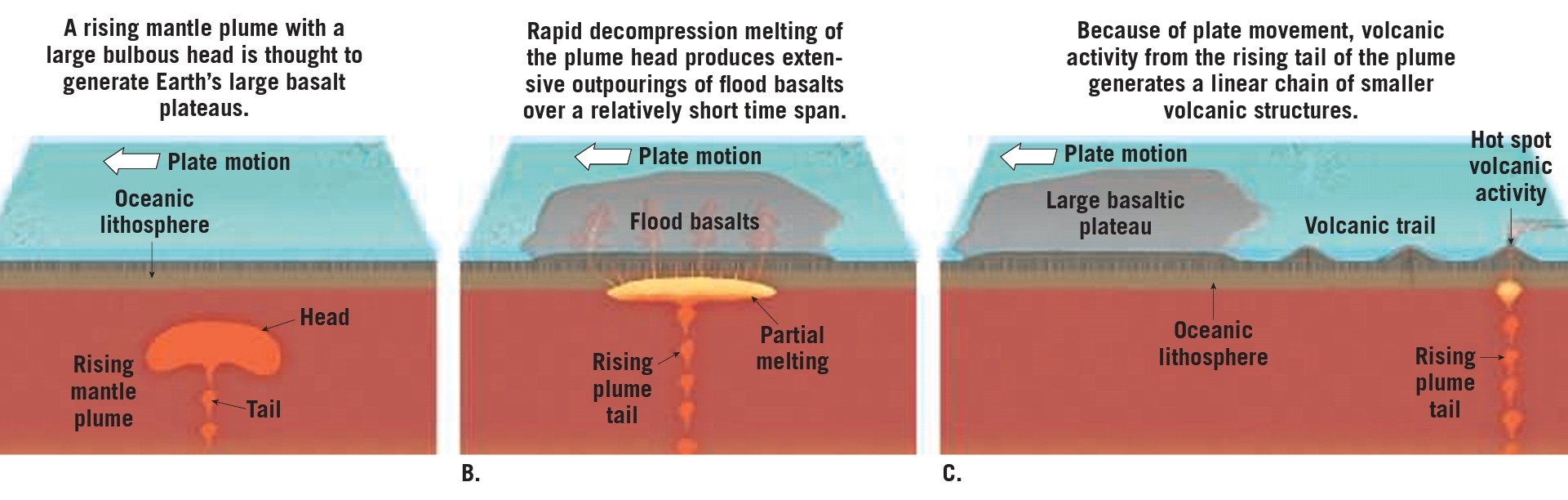
Intraplate volcanism (within the plate)
– Hotter than normal mantle material ascends upwards (mantle plume)
– It originates a the core-mantle boundary
– When the plume head reaches the top of the mantle, decompression melting produces basaltic magmia that initiates volcanism hot spot

The End
