Sulfides & Related Minerals
Sulfide & related minerals
form nearly 600 minerals, few are abundant
have great economic value
Metals essential for industrial society extracted from sulfide include copper, zinc, lead, antimony, molybdenum, cobalt, nickel, silver
sulfur are law δ- than O, have about 10-20% ionic character (covalent or metallic)
There is no agreed on classification scheme
General Formula
MpXr
M: metal or semimetal
Such as: Fe, Zn, Cu, pb, Sb, or As
X: atoms
Such as: S, As, S + As, or Te
Sulfosalts
metal + semi-metal + sulfur
classified based on chemical notions that have long since been abandoned
SULFIDE PARAGENESIS
Hydrothermal Deposits: sulfide & related minerals characteristic of hydrothermal vein & replacement deposits, deposited from hot aqueous solutions in void spaces or by replacement of rock
Essential features of hydrothermal system:
1. Water
2. Heat
3. Source for metals precipitated by water
4. Migration pathways
5. Precipitation site
Water: may be meteoric, magmatic, metamorphic, or connate
Heat: by igneous intrusion, & burial
Source for metals precipitated by water: sulfur derived from crystallizing magma or leached out of rock by water
Migration pathways: Fluids flow via rock along fault, fracture, & normal pore space
Precipitation site: Minerals precipitate by filling spaces along faults, fractures, & in other voids, or by replacing minerals in rock

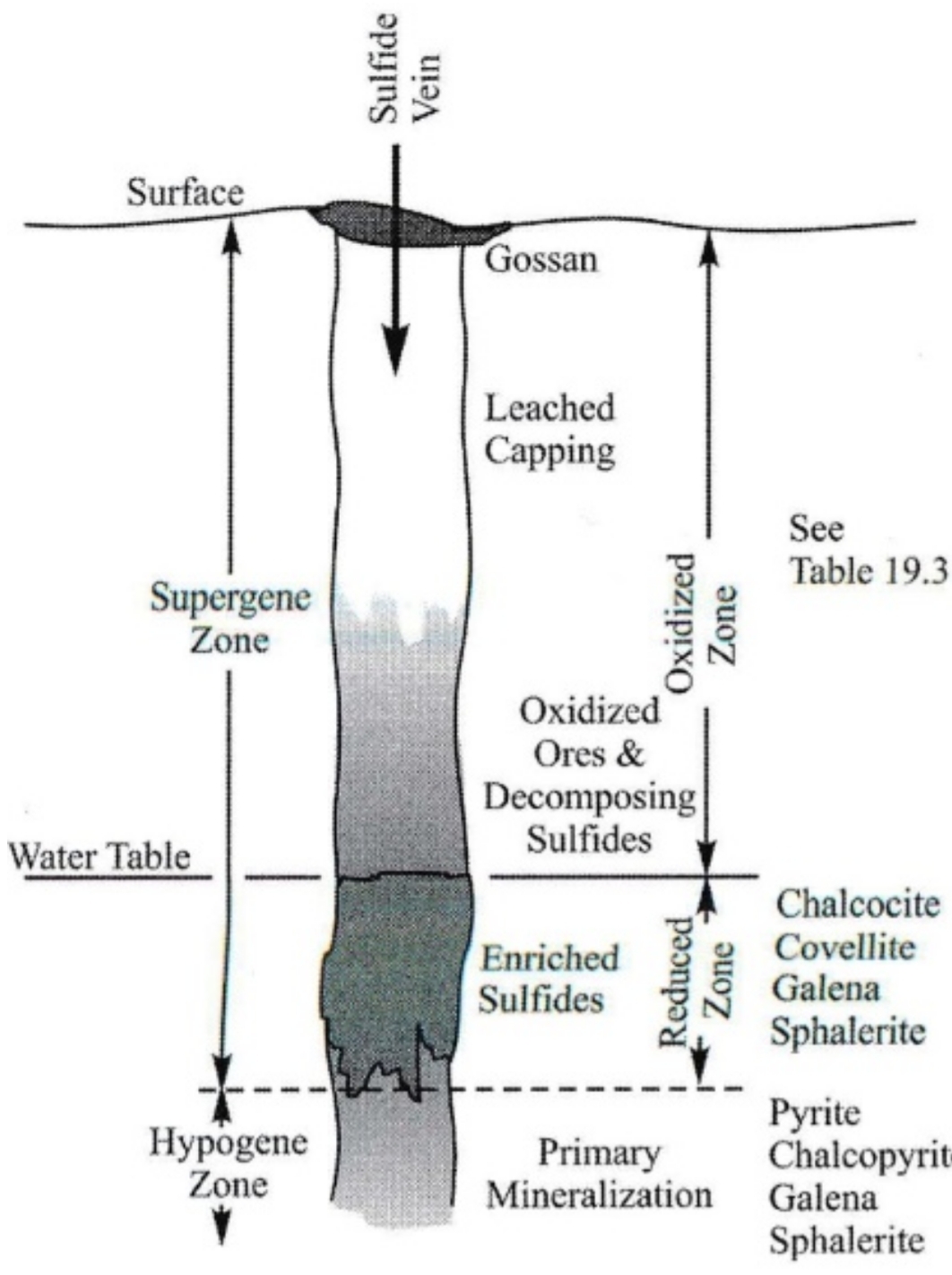
Supergene Processes
primary or hypogene mineralization produced in hydrothermal system extensively altered if exposed to nearsurface environment
metals found in sulfides form oxides, hydroxides, carbonates, & sulfates
Because reactions produce oxygen-bearing minerals at expense of sulfides, near zone is referred to as oxidized zone & result are called supergene or secondary minerals
Because pyrite are common sulfide, oxidized zones of most sulfide deposits colored yellow & red: iron oxides & hydroxide derived from it
These minerals insoluble & accumulate near surface to form encrusting mass “gossans”
Pyrite in deeper portions of super genealteration zone serve as host to extensive precipitation of copper sulfides in supergene enrichment process
sulfide-enriched or reduced zone: zone of concentrated mineralization at water table surface
Supergene processes cause extensive alteration of country rock hosting sulfide deposits
Excess acid produced by oxidation of sulfides neutralized by reaction with silicate & form clay
A typical reaction involves hydrolysis of K-feldspar (KAlSi₃O₈) to form kaolinite:
2KAlSi₃O₈ + 2H⁺ + H₂O
→ Al₂Si₂O₅(OH)₄ + 4SiO₂ + 2K⁺

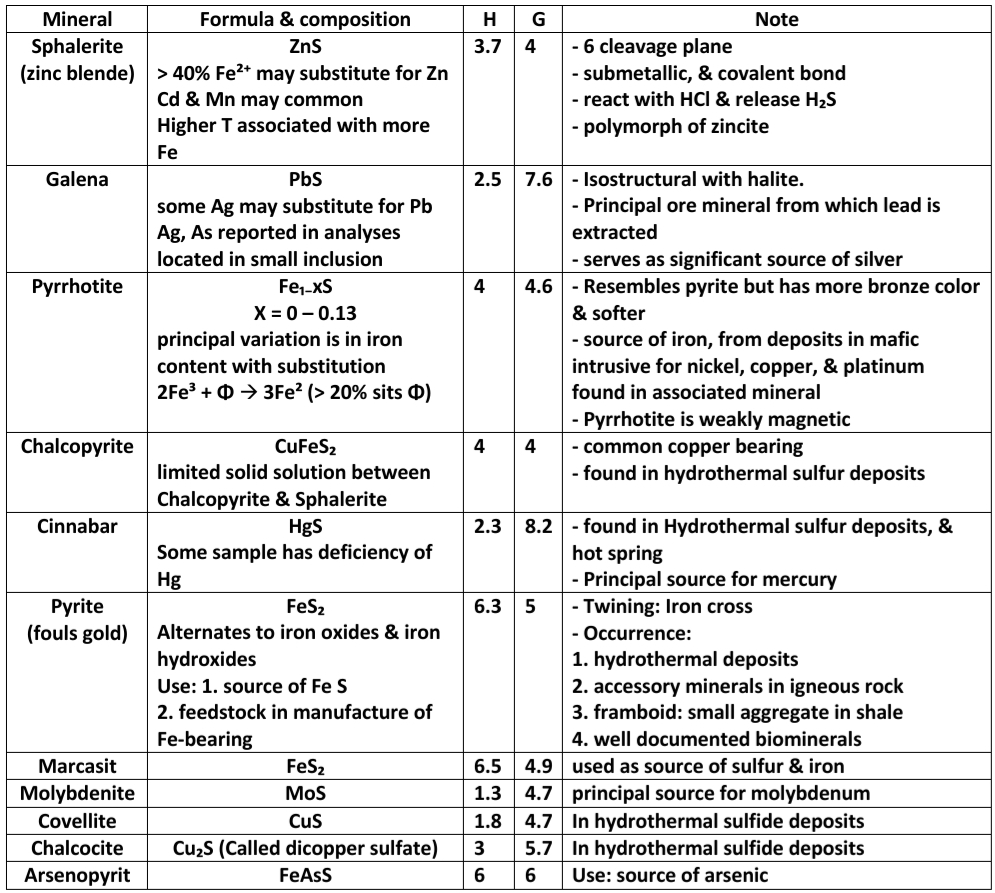
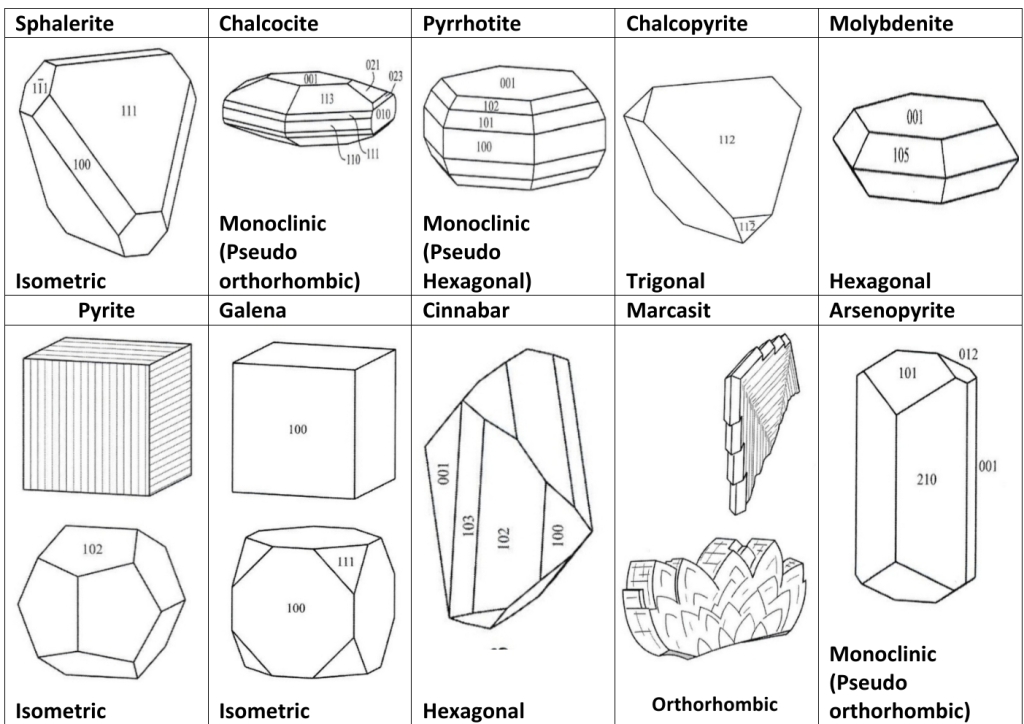
Pyrrhotite Vs Pyrite
In Pyrrhotite principal variation in iron content 2Fe³⁺ + Φ –> 3Fe²⁺ (> 20% Φ)
Pyrrhotite has more bronze color, & softer
Pyrrhotite weakly magnetic
The End
