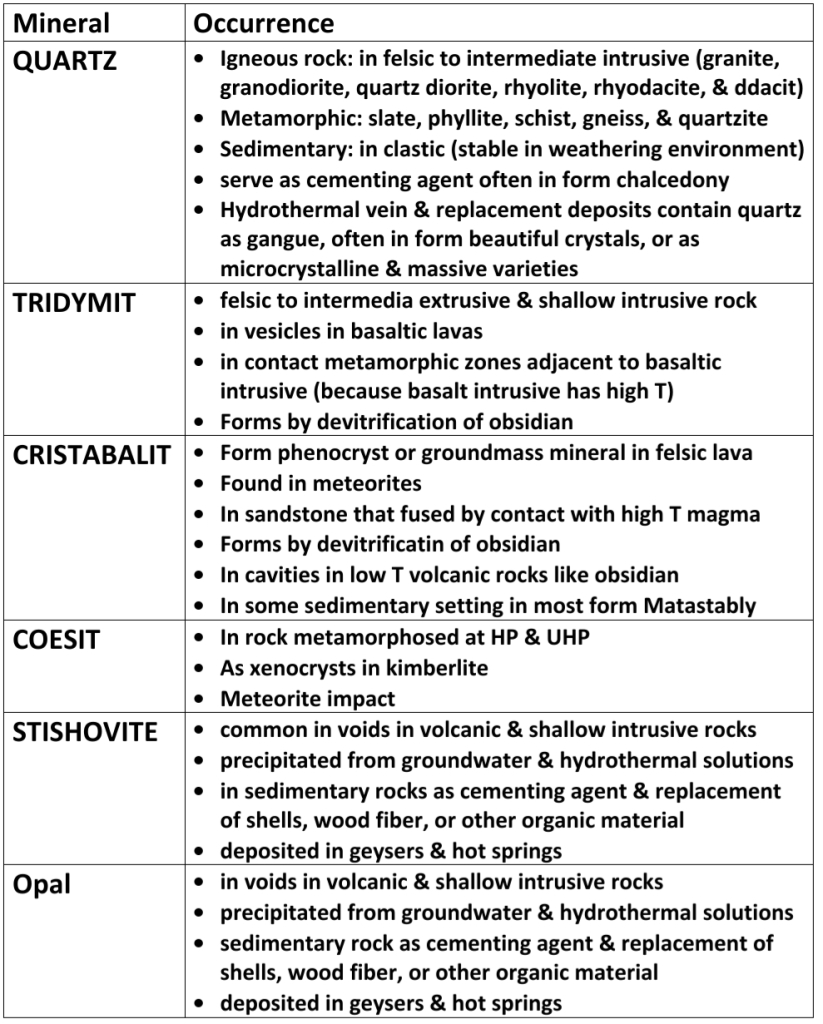
Part.1 : Silica Group SiO₂
Polymorphs
* 5 Polymorphs
– Quartz, Tridymite, & Cristobalite are common polymorphs
– Stishovite & Coesite are quite rare
Conversion between Quartz, tridymite, & cristobalite requires bonds be broken, they are reconstructive polymorphs
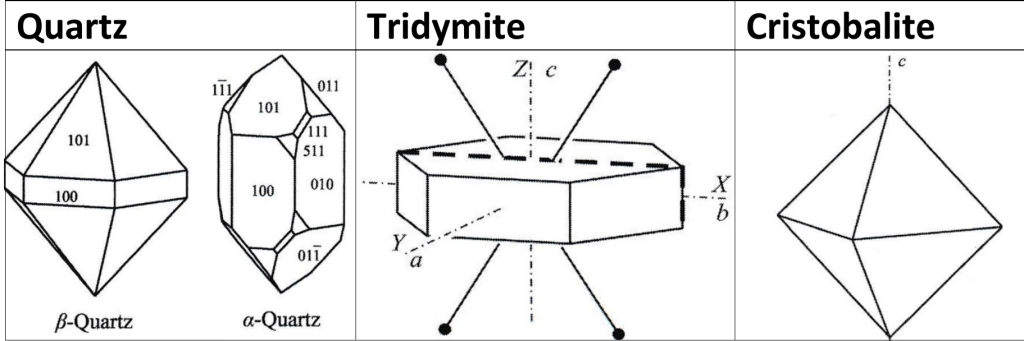
Quartz, Tridymite, & Cristobalite Structures represented by
1. α (low) varieties (Temperature, Symmetry)
2. β (high) varieties: has higher symmetry & stable at higher Temperature apolymorph
α & β varieties displacive polymorphs, related by distortion in lattice
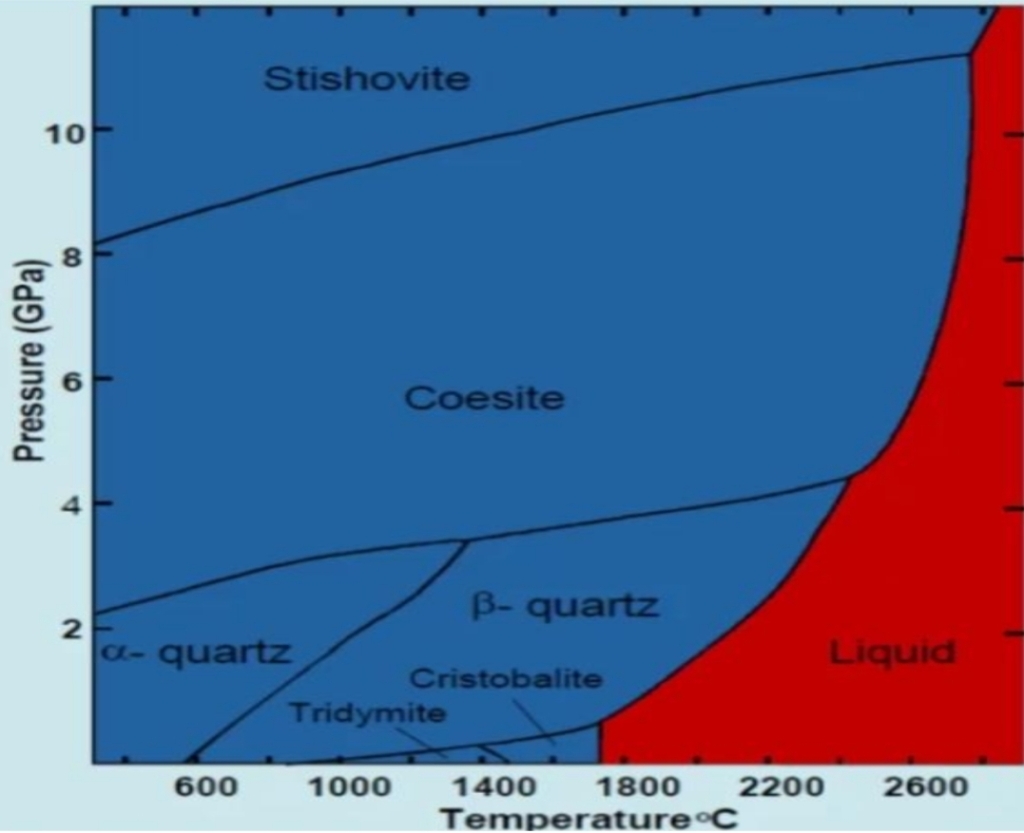
Forms of quartz, tridymite, & cristobalite at room T are α varieties
Tridymite & cristobalite grow only as β, Primary α-tridymite & α-cristobalite don’t
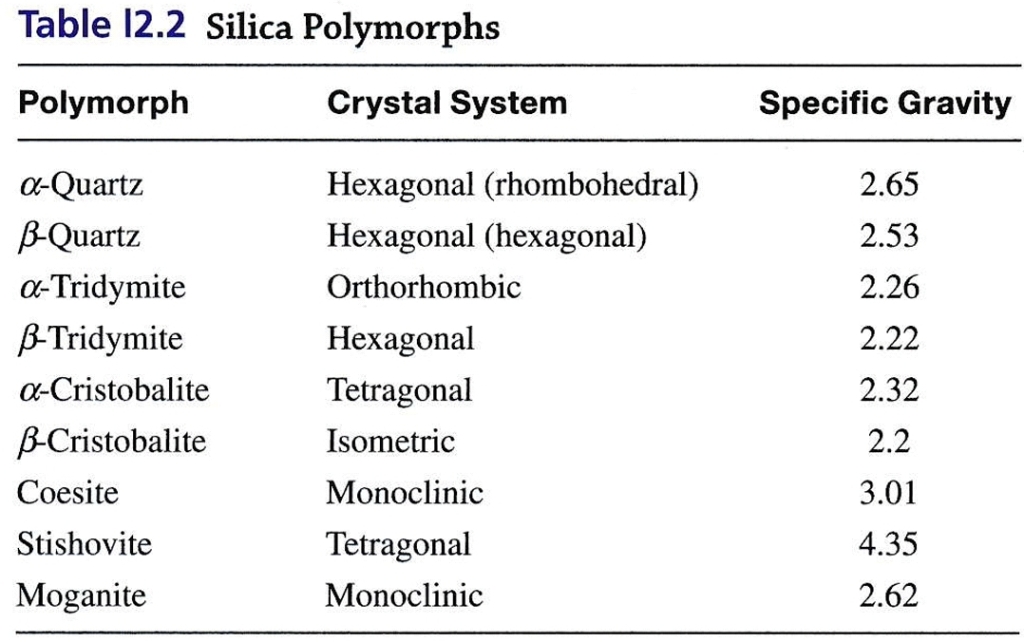
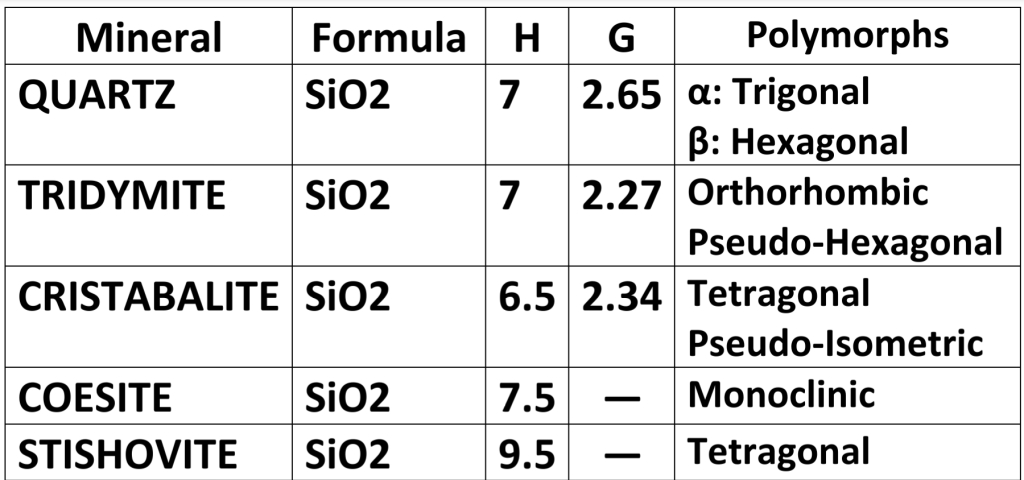
Chemical formula, specific gravity, Hardness, & crystal system
Quartz SiO₂
Twinning: Japan twin
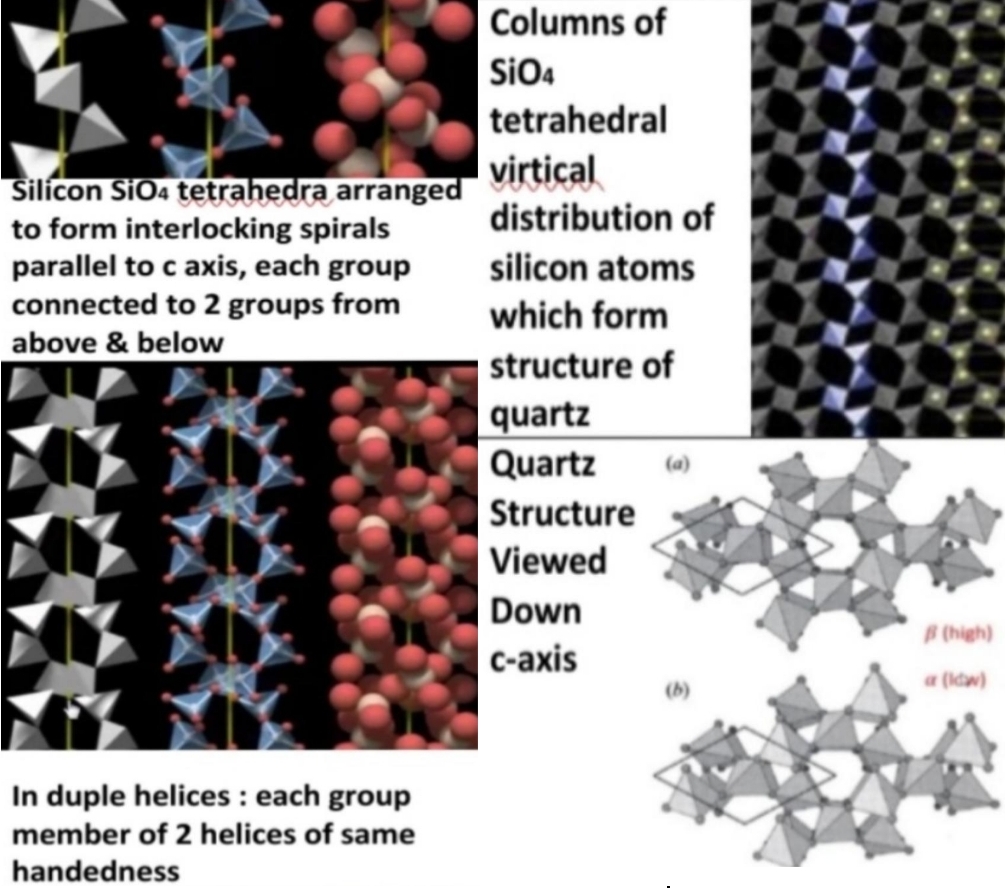
Symmetry: 6-fold screw
Crystal System: Hexagonal in β, Trigonal in α
Use:
1. making glass
2. source of silicon
3. semiconductors, abrasive or polish
4. semiprecious gemstone
Crystal forms: dipyramid + prism
Crystal habit &
-Anhedral in igneous & metamorphic rocks
– Detrital, & Crystals of α prismatic
Deformed quartz display pattern of undulatory extinction seen in Thin section due to defects (rotated stage → wave manner)
On cooling via transition T (573°C at 1atm)
β structure kinks so spirals reduced to 3-fold symmetry & point group is reduced to 32 forming α-quartz
Composition: pure SiO₂ but trace amounts of other elements may present
– Common substitution:
(Al³⁺, Fe³⁺) + (Na⁺, Li⁺, K⁺, H⁺) → Si⁴⁺
H form OH
Chert & Chalcedony
Quartz occurs in microcrystalline aggregates
Chert: fine granular microcrystalline quartz, found as nodules or irregular beds in limestone
Chalcedony: fibrous microcrystalline quartz & moganite
Moganite: varity of silica, consist of alternating sheet of right & left handed quartz, has H=6 & lower G due to open structure,
monoclinic crystal system
Quartz Color
variaty of color
common is colorless or gray
ROCK CRYSTAL: Clear crystals
AMETHYST: Violet or purple (due to Fe)
ROSE QUARTZ: Pink or rose red (due to uncertain, or inclusions)
CITRINE: Yellow (due to Fe, irradiation, or some combination)
MILKY QUARTZ: Milky white (due to fluid inclusions)
SMOKY QUARTZ: Smoky brown to black (due to color centers produced by irradiation of quartz containing trace amounts of Al)
JASPER: Red or brown microcrystalline quartz (Chert)
FLINT: Black or dark gray microcrystalline quartz (Chert)
AGATE: Microcrystalline quartz (Chalcedony)

Stishovite & Opal arn’t silicate