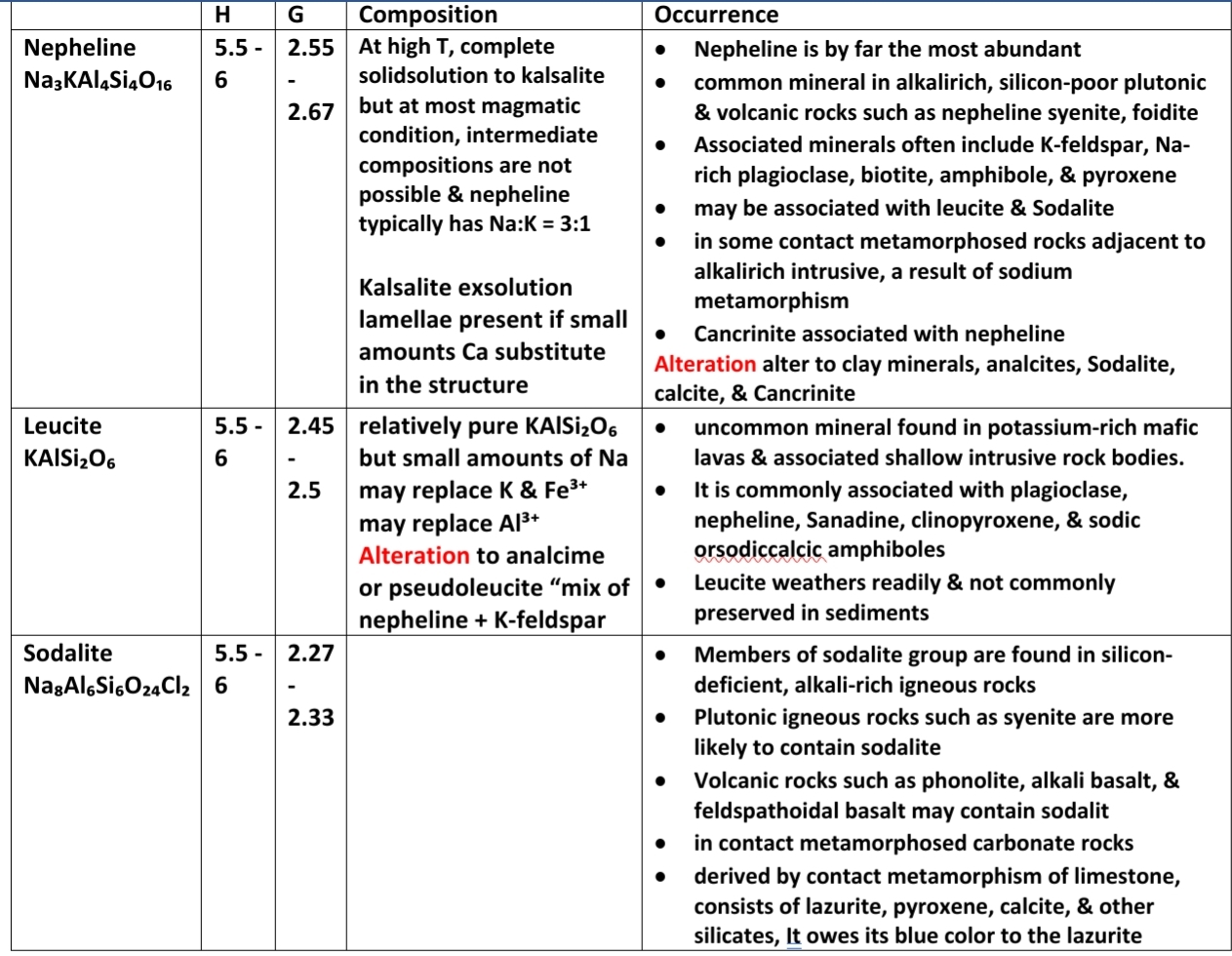
Part.3 : Other Framework Silicate
FELDSPATHOIDS
semilar to Pheldspare in strucure & physical properties
Structure: similar to feldspare consist of 4 & 6 member ring linked latterally to form 3D tetrahedra Framework (6 ring → more open structure → less G)
– is similar to tridymite
Chemically feldspathoids are distinguished from feldspars by having less silica relative to the amount of Na & K
Cavities created in framework of tetrahedra Occupied by Na & K
The principal occurrence of these minerals is in alkali-rich, silica-poor igneousrocks, & Because magmas of these compositions are uncommon, the feldspathoids also are uncommon
ZEOLITE GROUP
Largest single group of silicate & Contain major rock forming mineral : Contains over 80 naturally occurring members & roughly 600 additional synthetic zeolites with no natural counter part
The structures consist of stable open frameworks of Al/Si tetrahedra that link together to form open channels & voids whose geometry is different in the different species.
– The water molecules & the mono- & divalent cations occupy the voids in theframework structure and are weakly bonded.
Zeolization : process in which extensive zeolite deposited formed in altered rock
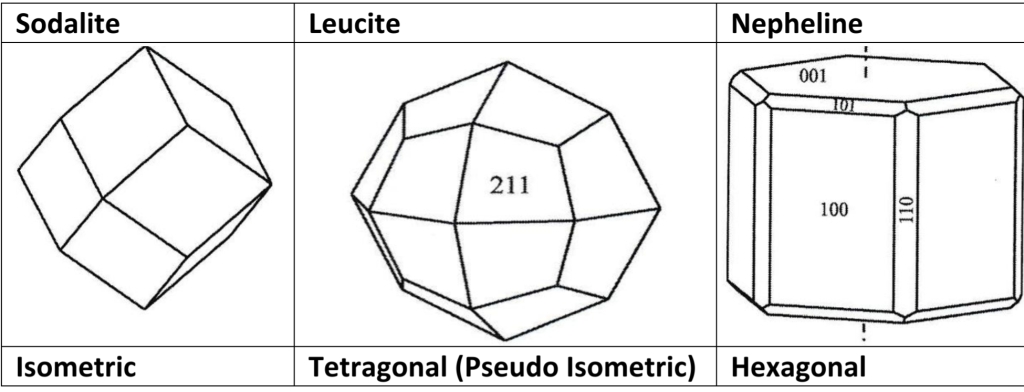
ANALCIME NaAlSi₂O₆•H₂O
– Equant trapezohedral crystals
LAUMONTITE CaAl₂Si₄O₁₂•4H₂O
CHABAZITE
– Rhombohedral (pseudocubic) crystals
HEULANDITE
– Platy crystals with perfect {010} cleavage
– often with a coffin-shaped cross section
NATROLITE
– Slender prismatic or acicular crystalsthat
– may form beautiful radiating aggregates
STILBITE
– Platy crystals tabular on {010} cleavage
– often forms sheaf-like aggregates
THOMSONITE
– Acicular, prismatic, or bladed crystals
– often in spherical, botryoidal, or columnar aggregates & masses that may be color zoned
Occurrence
– Analcime primary magmatic in basalt, phonolites, & related rock, & in other occurrences secondary
– Environment of zeolite:
1. weathering
2. alteration (with groundwater)
3. hydrothermal (with igneous activity)
4. sedimentary diagniss (volcanic ash), contact meta. & burial
5. low grade regional metamorphism
USE
– drying agent (remove water vapore from gasses such as carbon dioxide)
– molecular sieves (due to open structure)
– sorbent to oil spills, in petroleum refining, medical uses, control odor (because absorbing ammonia)
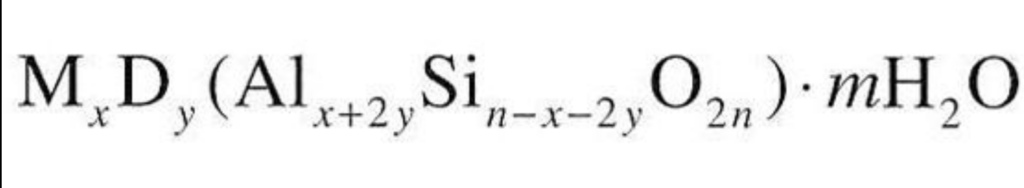
Zeolites are hydrated framework silicates
Where the ratio of Si to Al varies [1:1 – 6:1]
Commposition controled by parent rock
Felsc rocks → high Si content
mafic rocks → law Si content
Scapolite
Scapolite Na₄Al₃Si₉O₂₄Cl
Crystal system : tetragonal
H = 5 – 6
G = 2.50 – 2.18
Alteration Replaced by aggregates containing sericite, calcite, chlorite, epidote, zeolites, or otherminerals
Occurrence
– In regional & contact metamorphism rock derived from cacareous, or gabbroic
– May replace Plagioclase in Hydrothermal altered mafic igneous rock
The End
