Chapter One
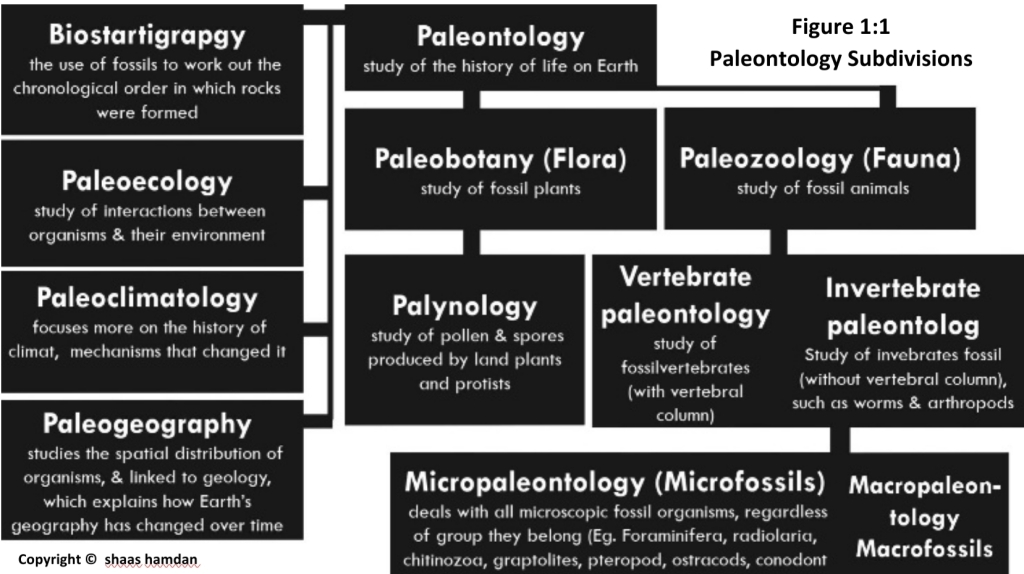
Paleontology
Paleontology: is the study of the history of the life on Earth as based on fossils (age, formation, & evolutionary)
Fossils: any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any living thing from a past
– are the key of understanding of past life
– give clues about organisms lived ago
– help to show that evolution has occurred
– provide evidence about how Earth’s surface was changed over time
Age of fossils: youngest from Holocene to the oldest from archaean (> 4.48Ga)
– Age of earth 4.6Ga, & the oldest fossils 3.5Ga
– most fossils are found in sedimentary rocks
– the oldest known fossils are cyanobacteria that produced structure called Stromatolites
The ancient atmosphere consists of CO, CO₂, H₂O, N₂, H₂, NH₃, CH₄, H₂S, & little free O₂


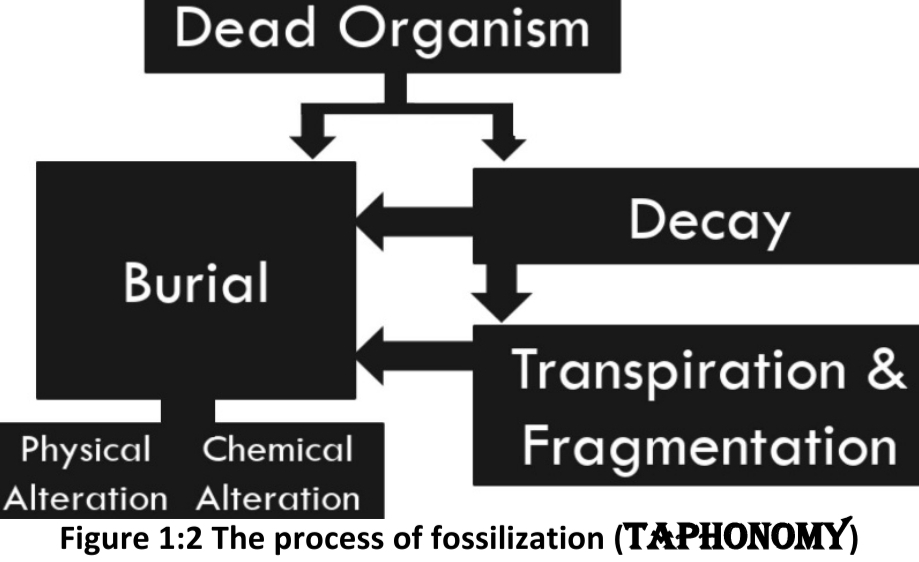
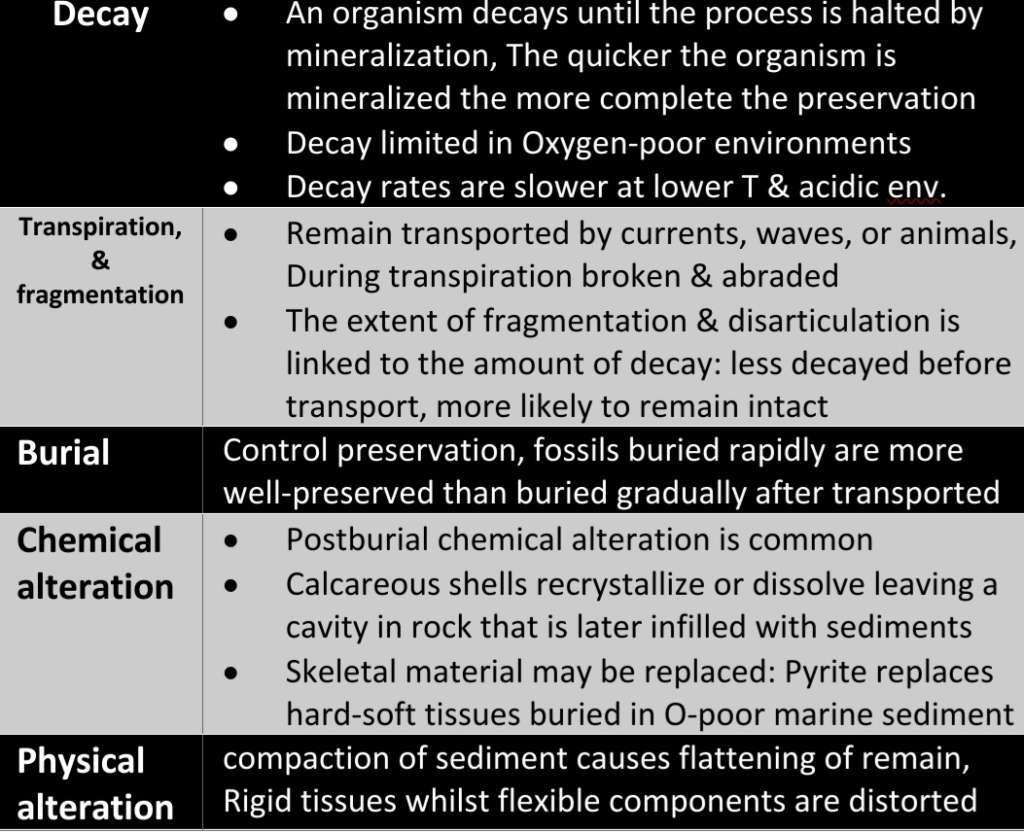
Conditions favorable for preservation
1. Rapid & permanent burial
2. Continued sediment accumulation
3. Lack of oxygen (O limits decay & scavenging)
4. Lack of heat or compression (destroy fossils)
5. Hard body parts (skeletal bones, exoskeletons)
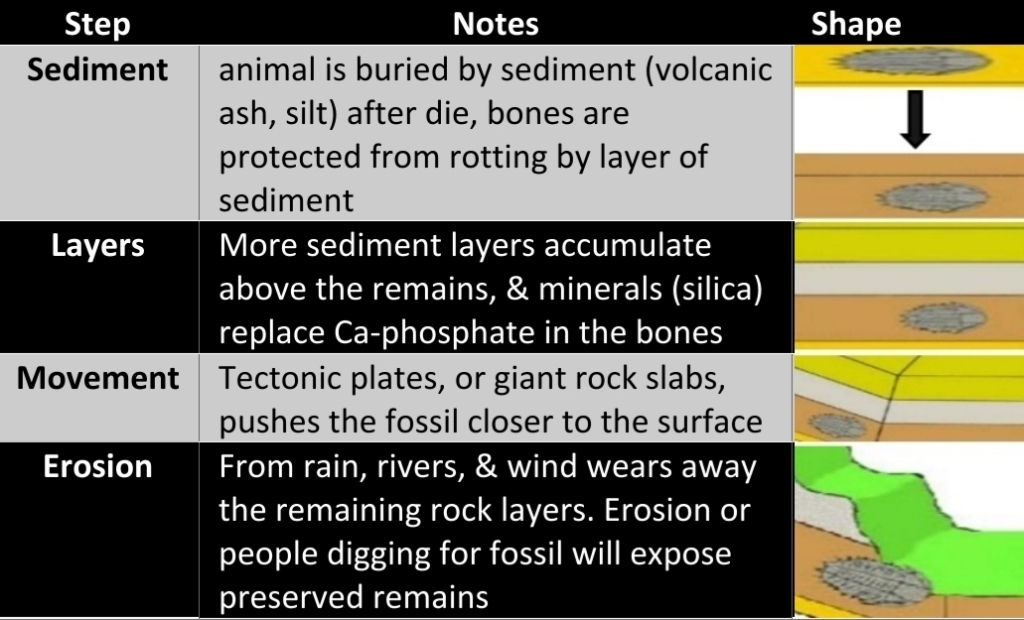
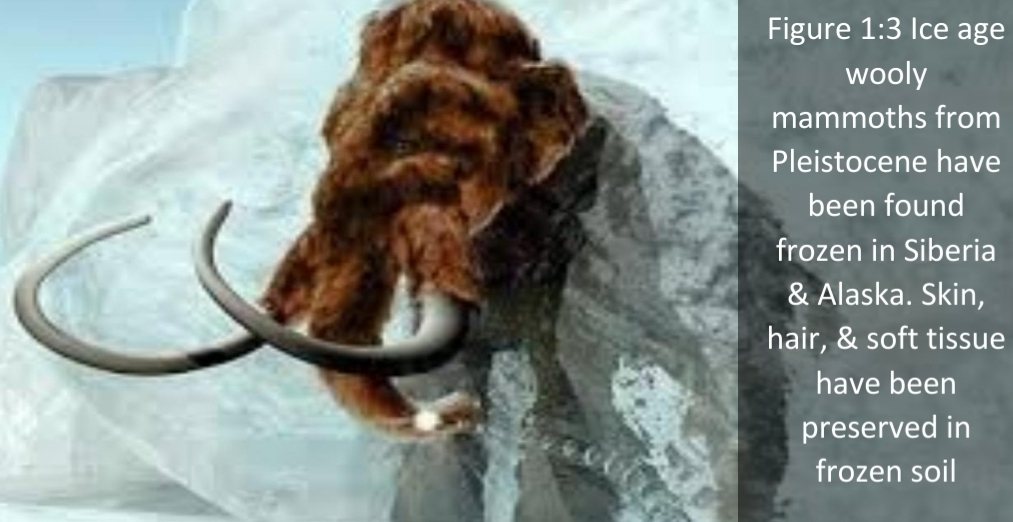
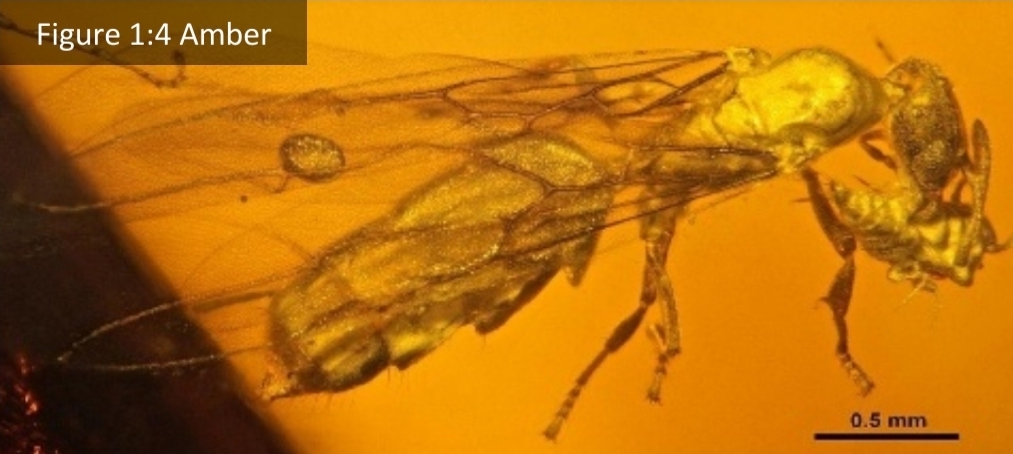
Body fossils
actual body or body fossils that preserved may be altered (chemically or physically)
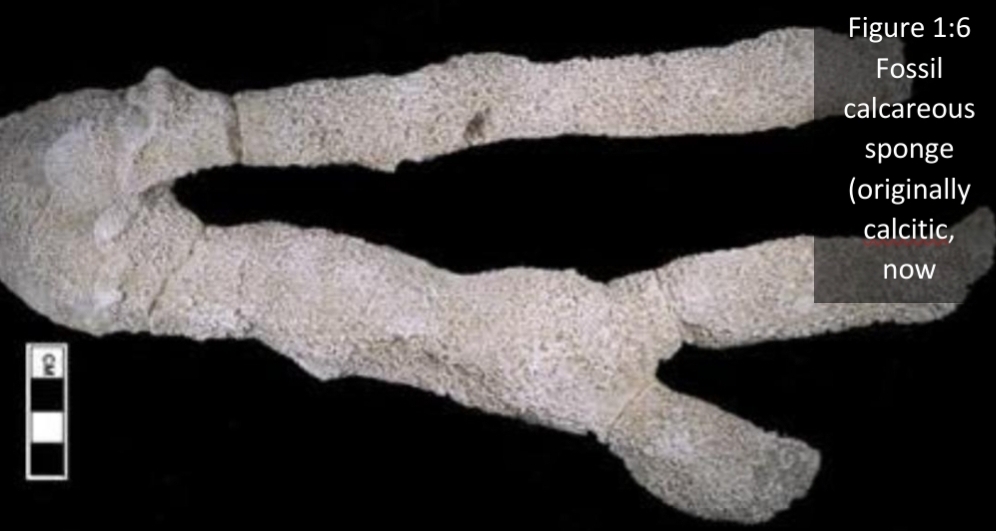







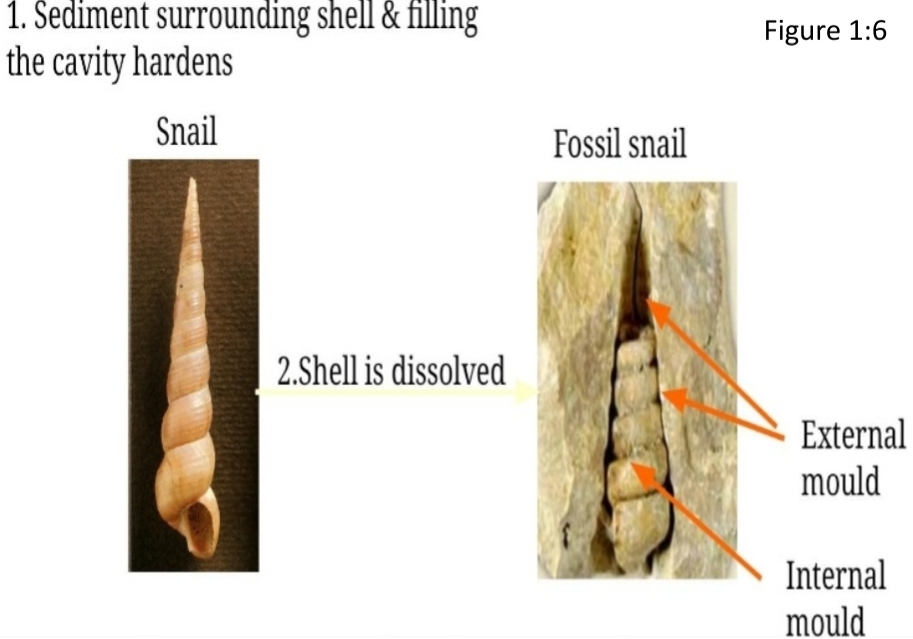
Molds & Casts
Mold & cast: 3D preservation where the original is not present
As remains buried, they surrounded with sediment
Mold impression of skeletal (or skin) remains in an adjoining rock
If buried object hollow, it infilled with sediment, the actual buried object decays or dissolved, leaving internal & external mould
Casts: are formed when an external mould is infilled by sediment or precipitated minerals
– appears as replica of original buried object
– cast is original skeletal material dissolves cavity (mold) fills with materials


The End
