Online Quiz
Quizlet
Geologic Time & Earth History
Important Terms
Relative: Know Order of Events But Not Dates, Such as Bedrock Formed Before The Glaciers Came
Relative age dates: placing rocks & geologic events in their proper sequence
Absolute or Numerical: Know Order & Dates of events
Absolute or Numerical dates: termed absolute age dating, actual age of geologic events
2 Conceptions of History
Catastrophism
– earth history dominated by violent events
– As.: great effects require great causes
– Catastrophes do happen but uncommon
Uniformitarianism earth history dominated by small-scale events typical of the present
– Assumption: we can use cause & effect to determine causes of the past events
principles of relative dating
– Developed by Nicolaus Steno in 1669
1. Superposition Law: In undeformed sequence of sedimentary or volcanic rocks, the oldest rocks at base; & youngest at top
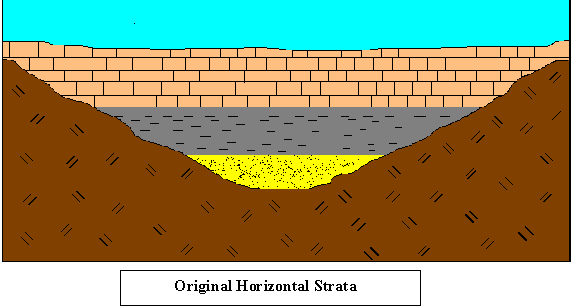
2. Principle of original horizontality: Layers of sediment deposited horizontally
– flat strata not disturbed by folding or faulting
3. Cross-Cutting Relationship Principle Younger features cut older once
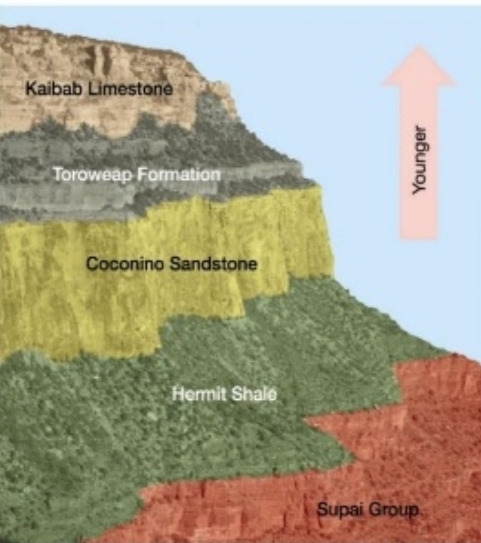
Superposition
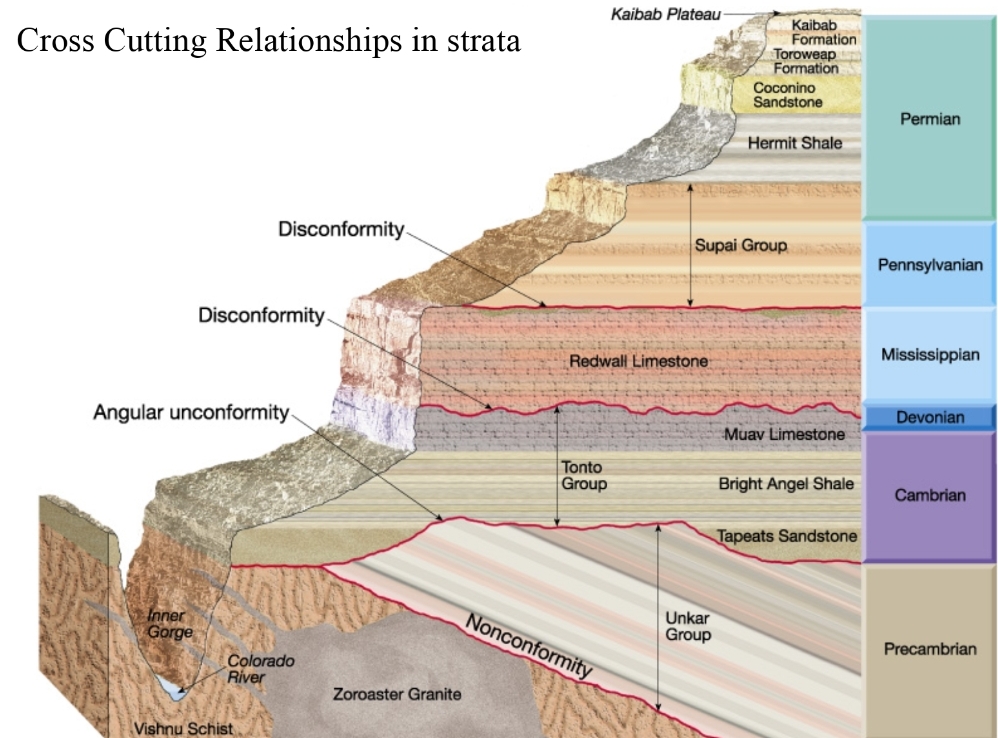
Cross-Cutting Relationship
correlation
Matching strata of similar ages in different regions
Principle of fossil (or faunal): Correlation relies upon fossils
succession fossil organisms succeed one another in a recognizable order, thus any time period is defined by the type of fossils in it

Unconformities
loss (or break) of the rock record
produced by erosion & nondeposition
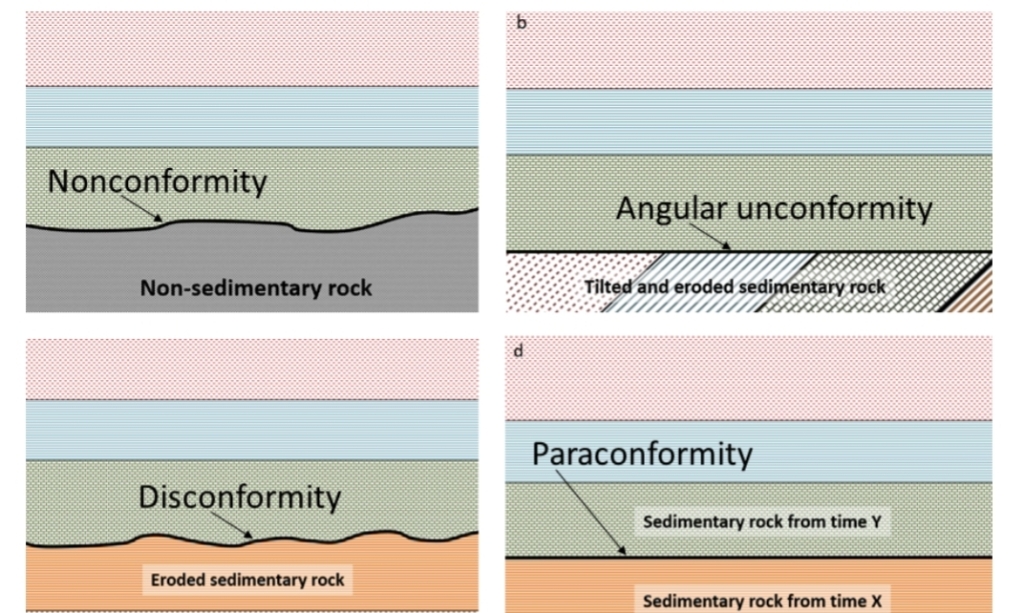
Types of unconformities
Angular unconformity
tilted rocks overlain by flat-lying rocks
– between 2 sequences of sedimentary rocks
Disconformity
strata on either side of the unconformity are parallel (but time is lost)
– between 2 sequences of sedimentary rocks
Nonconformity (basement)
sedimentary rocks deposited above metamorphic or igneous rocks
– between sedimentary rocks (above) & non-sedimentary rocks (below)

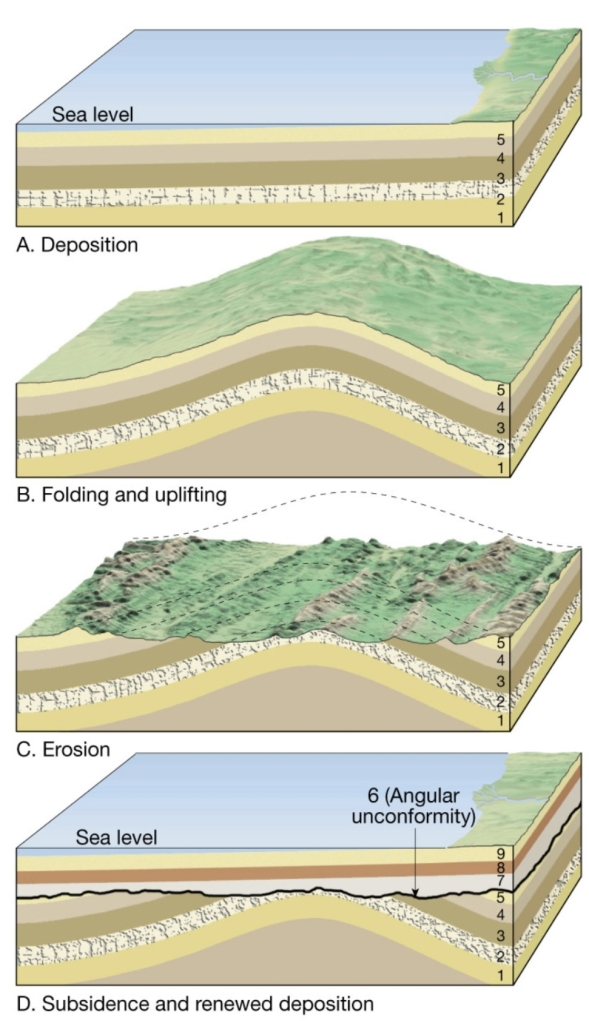
deposition horizontal strata → folding & uplifting → Erosion → subsidence, deposition


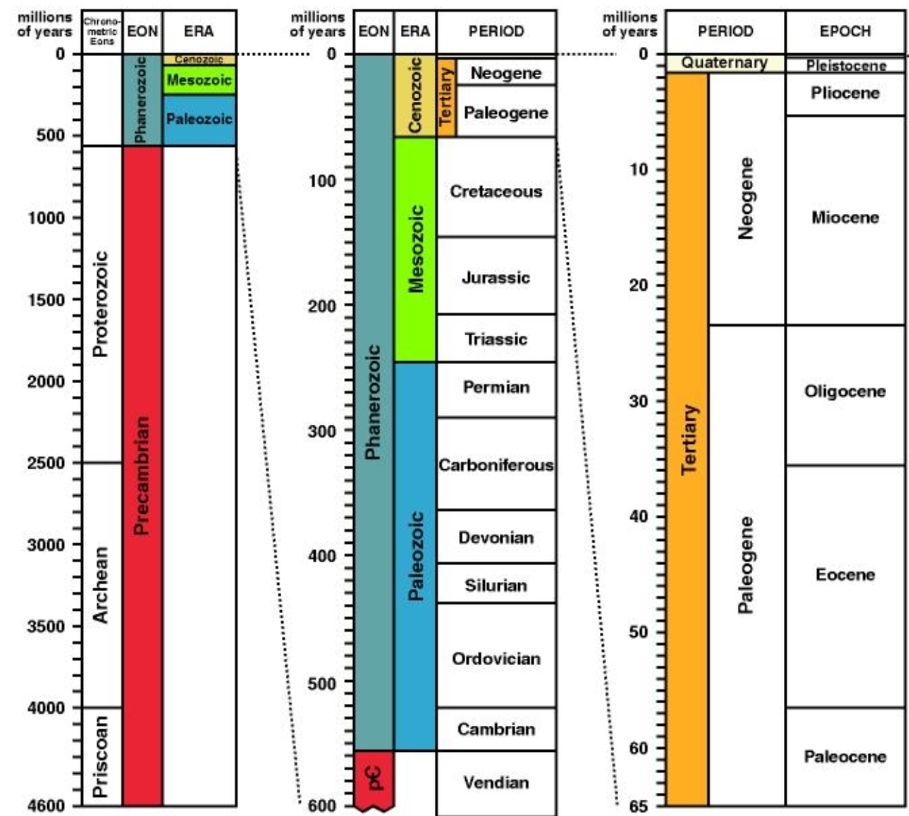
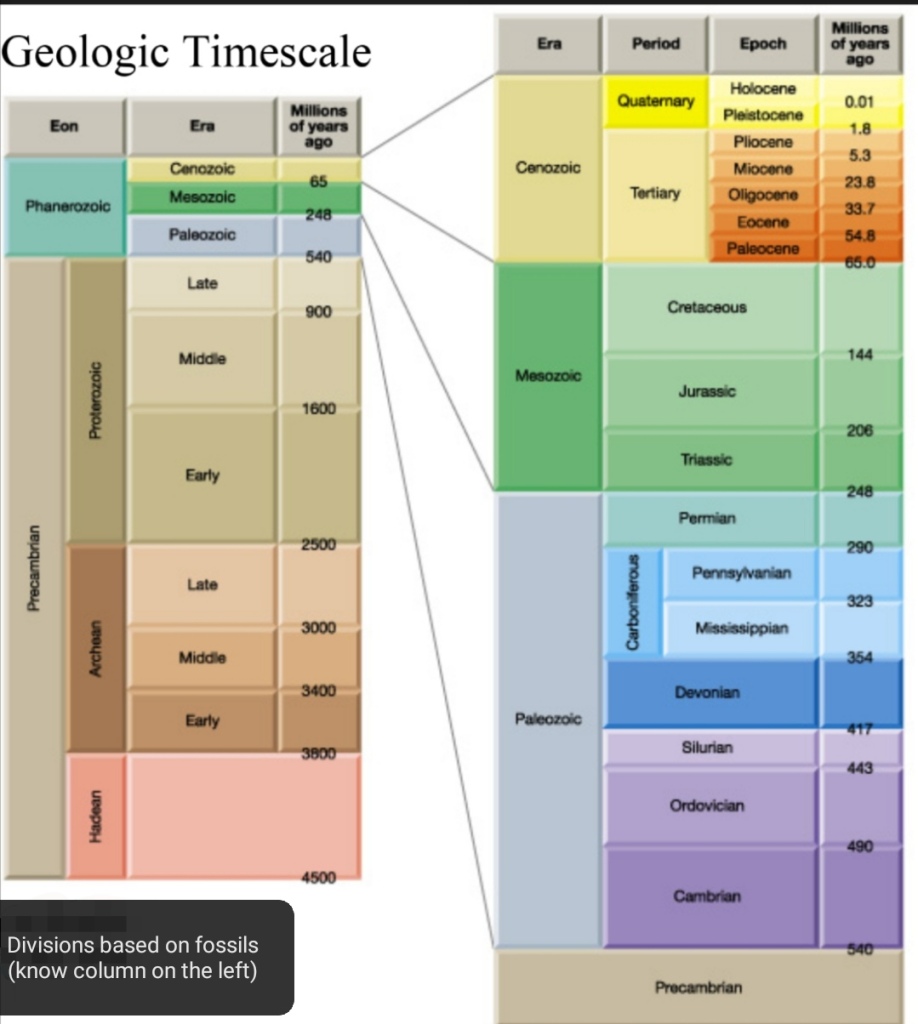
The geologic time scale
Is the calendar of Earth history, Subdivides geologic history into units, Originally created using relative dates
Structure of the geologic time scale:
Eon→Era→Period→Epoch→Age→Chron
– Era subdivision of an eon & subdivided into periods, Periods subdivided into epochs…atc
Eras of Phanerozoic eon:
1. Cenozoic (recent life)
2. Mesozoic (middle life)
3. Paleozoic (ancient life)
Precambrian time
– 4BY prior to Cambrian period
– Not divided into small time units because the events aren’t known in detail
– Immense space of time (Earth is ≈ 4.5BY)

Introduction to Radioactive Decay
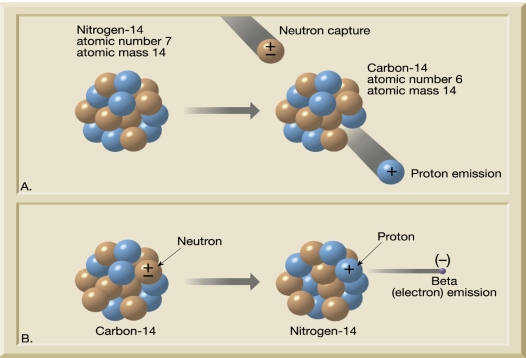
B. Beta emission
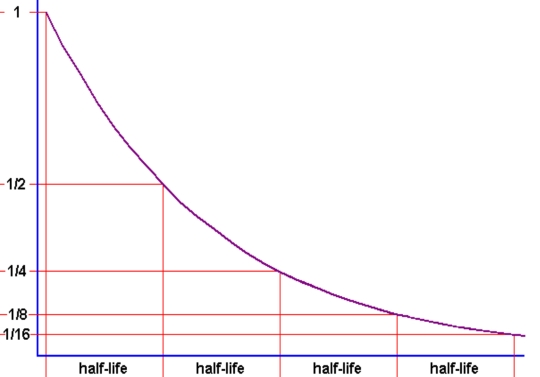

U-Pb decay curve
How much of the daughter element is remaining after 4 half lives?
What is the age of the sample?
